In logistics management, accurate information flow between trading partners is crucial. One of the key elements facilitating this is the Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN). Specifically, the Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) 856 document plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operations and efficient inventory management. This blog delves into the concept of the advanced shipping notice, its importance, and the specifics of EDI 856.
What is an Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN)?
An advanced shipping notice is an electronic notification sent by a supplier to a retailer or buyer before the shipment arrives. It provides detailed information about the shipment’s contents, including the products, quantities, and expected arrival times. ASN in the supply chain allows the recipient to prepare for the incoming goods, streamline receiving processes, and ensure accurate inventory management. This is the advanced shipping notice example.
Importance of Advanced Shipping Notice
An Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN) is an electronic document that provides detailed information about a pending delivery before the shipment arrives at its destination. It is most commonly transmitted using EDI 856, one of the standard documents in Electronic Data Interchange systems. ASNs serve as a bridge between the supplier and the buyer, enabling seamless coordination in receiving and inventory processes. Implementing ASNs in logistics and supply chain operations brings a multitude of benefits. Here’s a closer look at why ASNs are essential for efficient and modern supply chain management:
1. Improved Inventory Management
Accurate inventory planning and real-time visibility.
- What It Means: ASNs give supply chain managers prior notice of what items are being shipped, how many, and when they’ll arrive.
- Why It Matters: With this information in hand, businesses can:
- Plan replenishment cycles
- Reduce stockouts and overstock scenarios
- Update inventory levels ahead of physical receipt
- Real-World Impact: Retailers can optimize shelf stocking, eCommerce companies can better forecast demand, and manufacturers can align production schedules with incoming materials.
2. Enhanced Receiving Efficiency
Streamlined inbound logistics and warehouse operations.
- What It Means: ASNs allow receiving teams to prepare ahead of time, optimizing warehouse workflows.
- Why It Matters: Knowing exactly what is arriving helps:
- Allocate dock or shelf space in advance
- Schedule labor shifts and allocate equipment like forklifts
- Reduce congestion at receiving docks
- Real-World Impact: Faster unloading, shorter lead times, and reduced labor hours lead to quicker turnover and lower operational costs.
3. Reduced Shipment and Receiving Errors
Improved accuracy during the receiving process.
- What It Means: ASNs contain structured data including product SKUs, quantities, packaging details, and serial numbers.
- Why It Matters: This allows receiving teams to:
- Cross-check incoming goods with the ASN and purchase order
- Identify discrepancies before goods enter inventory
- Minimize incorrect shipments, missing items, or duplication
- Real-World Impact: Lower reverse logistics costs, minimized disputes, and better supplier performance tracking.
4. Better Customer Service and Fulfillment
Accurate delivery commitments and proactive communication.
- What It Means: Businesses are better equipped to manage customer expectations with reliable shipment tracking and timelines.
- Why It Matters: With ASN data, companies can:
- Provide customers with real-time updates and estimated delivery times
- Improve order fulfillment accuracy and on-time delivery rates
- Communicate delays or substitutions in advance
- Real-World Impact: Elevated brand trust, stronger customer relationships, and increased customer satisfaction.
5. Enables Automation and System Integration
Supports digital transformation in supply chain operations.
- What It Means: ASN data integrates seamlessly with warehouse management systems (WMS), transportation management systems (TMS), and ERP platforms.
- Why It Matters: This enables:
- Automated goods receipt and inventory updates
- Barcode scanning and electronic putaway
- Electronic proof-of-delivery (ePOD) generation
- Real-World Impact: Higher efficiency with minimal human intervention, dramatically reducing operational errors.
6. Helps with Compliance and Penalty Avoidance
Supports retailers and distributors in meeting strict compliance guidelines.
- Real-World Impact: Strengthens supplier-retailer relationships and ensures adherence to logistics service level agreements (SLAs).
- What It Means: Many major retailers mandate ASN compliance as part of their vendor requirements.
- Why It Matters: Accurate and timely ASNs can: Help suppliers avoid chargebacks and penalties and Ensure proper labeling and documentation upon delivery.
Understanding EDI 856
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the electronic exchange of business documents between trading partners in a standardized digital format. Among the various EDI document types used in logistics and supply chain operations, EDI 856 plays a crucial role. Also known as the Advance Ship Notice (ASN) or Ship Notice/Manifest, it provides detailed information about a shipment before it physically arrives at its destination.
What is EDI 856?
EDI 856 is a standardized electronic document that communicates key details about an upcoming shipment from the supplier to the buyer. It helps the receiving party prepare in advance by providing visibility into what is being shipped, when it will arrive, and how it is packed.
The ASN is typically used in industries such as retail, manufacturing, logistics, and wholesale distribution, where accurate and timely receiving of goods is essential.
Why is EDI 856 Important?
The EDI 856 document is critical for:
- Streamlining receiving operations
- Automating inventory updates
- Improving warehouse planning
- Reducing receiving errors and delays
- Maintaining transparency and accountability
It enables organizations to match inbound shipments with purchase orders and prepares them to manage workload and inventory effectively.
Key Components of an EDI 856 Document
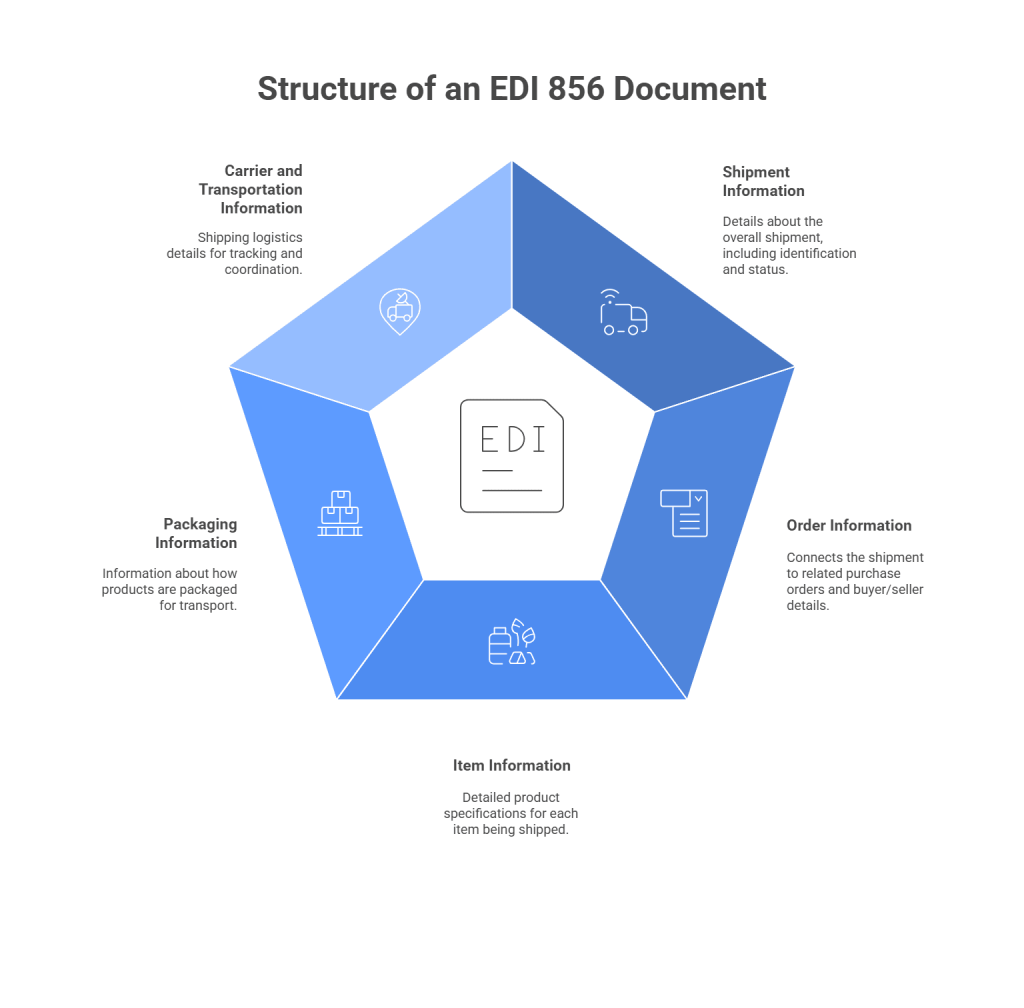
The EDI 856 contains multiple hierarchical levels of information, organized from shipment level to package level. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its core components:
1. Shipment Information
Details about the overall shipment, including:
- Shipment identification number
- Ship date and time
- Shipment status
- Shipping location and destination address
- Estimated delivery date
2. Order Information
This section connects the shipment to its related purchase orders, typically including:
- Purchase order number(s)
- Order date
- Buyer and seller information
- Sales order references
3. Item Information
Detailed product specifications for each item being shipped:
- Item numbers or SKUs
- Product descriptions
- Shipped quantities per item
- Unit of measure (e.g., pieces, kilograms)
- Lot or serial numbers (if applicable)
4. Packaging Information
Information about how the products are packaged for transport:
- Number and types of containers or packages (e.g., cartons, pallets)
- Pallet configuration and hierarchy
- Package identifiers (e.g., License Plate Numbers or SSCCs – Serial Shipping Container Codes)
5. Carrier and Transportation Information
Shipping logistics details provided for tracking and coordination:
- Carrier name
- Mode of transportation (truck, rail, air, etc.)
- Bill of lading number or tracking number
- Freight terms
How EDI 856 Works in the Supply Chain
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the typical EDI 856 workflow:
- Order Placement
The buyer (e.g., a retailer or distributor) sends a purchase order (EDI 850) to the supplier. - Preparing Shipment
The supplier picks, packs, and prepares the goods for shipment based on the order. - Generating EDI 856
Before the shipment leaves, the supplier generates an EDI 856 document containing all shipment-related details. - Transmission to the Buyer
The EDI 856 is transmitted electronically to the buyer’s EDI system or warehouse management system (WMS). - System Integration
The buyer’s system receives and processes the EDI 856 data to:- Update inventory
- Schedule receiving staff
- Pre-print barcode labels
- Plan warehouse space allocation
- Goods Receipt
When the shipment arrives, the buyer cross-checks the products against the EDI 856 to verify accuracy before completing the receipt.
EDI 856 Example – Real-World Scenario
To better understand how the EDI 856 Advance Shipping Notice (ASN) benefits both suppliers and buyers, let’s look at a practical, real-world use case involving a retail company and a beverage supplier.
Scenario: Beverage Delivery to a National Retailer
A major retail chain places a purchase order with a beverage supplier for 100 cases of bottled juice. Here’s how the EDI 856 document supports a smooth and accurate shipping process:
Step 1: Order Fulfillment
The supplier receives the purchase order and begins preparing the shipment.
- They organize the 100 juice cases across 10 pallets.
- Each pallet is assigned a unique Serial Shipping Container Code (SSCC) for individual identification and traceability.
Step 2: Creating the EDI 856 Document
Before the shipment is dispatched, the supplier generates an EDI 856 document that includes key information such as:
- Shipment ID – A unique identifier for the shipment
- Purchase Order Reference – To link the shipment back to the buyer’s original order
- Product Details – Including item types, quantities, and units of measure
- Packaging Structure – Demonstrating how items are grouped and packed (cases, cartons, pallets)
- Carrier Information – Including the transportation method, carrier name, and tracking number
- Planned Shipment and Delivery Dates – So the buyer knows what to expect and when
Step 3: Electronic Transmission of the ASN
Once the document is ready, the supplier sends the EDI 856 electronically to the retailer.
This happens before the shipment is physically dispatched, allowing the retailer to prepare in advance.
Step 4: Retailer Prepares for Delivery
Upon receiving the ASN, the retailer’s Warehouse Management System (WMS) automatically processes the document.
This allows the warehouse team to:
- Update inbound inventory records
- Allocate dock space for the incoming shipment
- Schedule staff and material-handling equipment for efficient unloading
Step 5: Shipment Arrival and Verification
When the delivery truck arrives, the receiving team refers to the data in the EDI 856 to verify the shipment.
- They scan the SSCC labels on each pallet.
- The received goods are cross-checked against the information in the ASN to confirm accuracy.
- Any issues or discrepancies can be flagged immediately and resolved efficiently.
Outcome :
Using EDI 856, the entire process—from order preparation to final verification—is streamlined, transparent, and highly efficient.
Both the supplier and retailer benefit from:
- Faster receiving
- Fewer manual errors
- Up-to-date inventory visibility
- Improved coordination across the supply chain
This example demonstrates how EDI 856 improves operational efficiency, enhances communication, and ensures accurate delivery—making it a critical component of modern logistics and supply chain management.
Benefits of Using EDI 856
- Efficiency: Automating the exchange of shipment information speeds up the process, reducing manual data entry and associated errors.
- Accuracy: EDI 856 provides precise and detailed information about shipments, ensuring that all parties have the correct data.
- Cost Savings: By reducing errors and streamlining processes, businesses can save on labour costs and avoid penalties for incorrect shipments.
- Visibility: EDI 856 enhances visibility into the supply chain, allowing for better tracking and management of shipments.
- Compliance: Many large retailers require suppliers to use EDI 856, making it essential for compliance and maintaining good business relationships.
Implementing Shipment Solutions
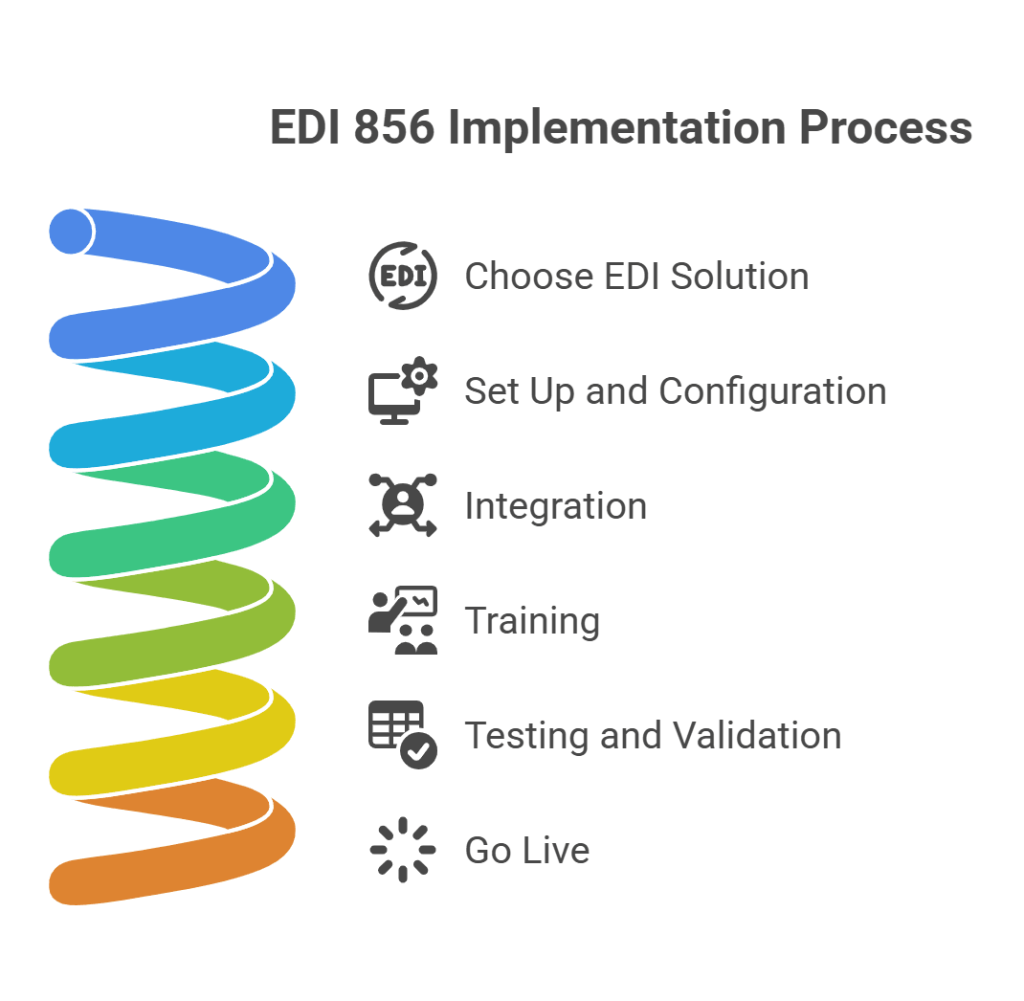
Implementing EDI 856 involves several steps, from choosing the right EDI software to integrating it with existing systems and training staff. Here’s a brief overview of the implementation process:
1) Choose an EDI Solution
Select an EDI provider that offers robust support for EDI 856 and other relevant documents. The solution should be scalable, secure, and compatible with your existing systems.
2) Set Up and Configuration
Configure the EDI software to align with your business processes and data requirements. This includes setting up communication protocols, data mapping, and testing the system.
3) Integration
Integrate the EDI solution with your ERP, WMS, or inventory management system to ensure seamless data flow and real-time updates.
4) Training
Train your staff on how to use the EDI system, including how to generate, send, receive, and process EDI 856 documents.
5) Testing and Validation
Conduct thorough testing with your trading partners to ensure the EDI 856 documents are accurate and the system is functioning correctly.
6) Go Live
Once testing is complete, go live with the EDI 856 implementation. Monitor the system closely during the initial phase to address any issues promptly.
Conclusion
The advanced shipping notice, facilitated by EDI 856, is a critical component in modern supply chain management. It enables efficient, accurate, and timely communication between trading partners, leading to improved inventory management, enhanced receiving processes, and better customer service. Do you want to optimise your inventory tracking? Get a host of solutions with Qodenext, your trusted ally in supply chain management.
FAQs: Understanding Advanced Shipping Notice and EDI 856
1. What is an Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN)?
ASN is an electronic notification sent by a supplier to a buyer or retailer before the shipment arrives. It contains detailed information about the contents, quantities, and expected arrival time of the shipment, allowing the recipient to prepare for the delivery.
2. Why is an Advanced Shipping Notice important?
It is crucial for several reasons:
- It improves inventory management by providing visibility into incoming shipments.
- It enhances receiving efficiency by allowing warehouses to prepare for incoming goods.
- It reduces errors by enabling cross-verification of received goods against the purchase order.
- It helps in offering better customer service with accurate delivery timelines.
3. What is EDI 856?
EDI 856, also known as the Ship Notice/Manifest, is an electronic document used for transmitting advanced shipping notices. It provides detailed information about a shipment, including shipment identification, order information, item details, packaging, and carrier information.
4. How does EDI 856 work?
When a supplier prepares a shipment, they generate an EDI 856 document containing all relevant shipment details. This document is electronically sent to the buyer’s EDI system, which processes and integrates it with the buyer’s warehouse or inventory management system. This automated process ensures accuracy and up-to-date information, reducing manual errors.
5. What are the benefits of using EDI 856?
Increased efficiency through automation, enhanced accuracy with detailed shipment information, cost savings by reducing manual labour, and avoiding penalties and improved supply chain visibility.
6. How can a business implement EDI 856?
Implementing EDI 856 involves:
- Choosing an EDI solution provider that supports EDI 856.
- Setting up and configuring the EDI software.
- Integrating the EDI solution with existing systems like ERP or WMS.
- Training staff on how to use the EDI system.
- Conducting thorough testing with trading partners.
- Going live and monitoring the system during the initial phase.
7. Can small businesses benefit from using EDI 856?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from using EDI 856. It helps streamline their supply chain operations, reduce errors, improve inventory management, and enhance relationships with trading partners. Additionally, many large retailers require suppliers to use EDI 856, making it essential for compliance and maintaining business relationships.







