In logistics and warehouse world, efficiency is the king. The introduction of RFID technology (Radio-Frequency Identification) has transformed the business providing never before seen visibility and control over inventory, assets and supply chain processes. As the global RFID market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 12.06% to reach a value of $25.24 billion by 2033, companies that adopt RFID tracking solutions are achieving up to 27% improvement in inventory accuracy and 40% faster order fulfillment.
The logistics industry’s adoption of RFID technology is a vital asset for continual improvement, as it has the potential to revolutionize supply chain processes. In this all-inclusive guide you will learn how RFID systems work, real world use cases, proven advantages and →Implementation Strategies to help you make an informed decision if RFID is right for your logistics operations.
Understanding RFID in Logistics
What Does RFID Stand For?
The full form of RFID is Radio-Frequency Identification. It employs radio waves to identify and track information stored on tags that are attached to objects — without requiring that the tags be scanned in a direct line of sight.
What is RFID?
RFID is a technology that employs radio waves to communicate data between a reader and an RFID tag. An RFID tag contains electronically stored information, which can be wirelessly transmitted to a reader or scanner. This technology has been widely adopted across various industries, including logistics and warehousing, due to its versatility and efficiency.
How Does RFID in Logistics Work?
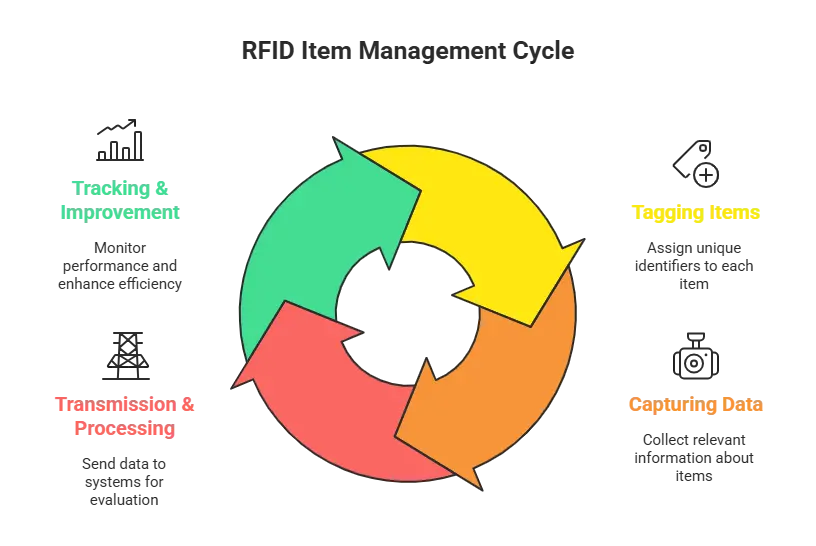
RFID in logistics works by the tag and reader communicating continuously through radio waves. Here’s how step by step:
- Tagging Items: RFID tags with a unique identification code are placed on the products or assets.
- Capturing the Data: RFID readers broadcast radio waves that power up tags within their proximity, allowing them to be automatically scanned — even if they’re in boxes or on the move.
- Transmission & Processing: The tag transmits information back to the reader, which forwards it to the central system or warehouse management application.
- Tracking & Improvement: The data is continuously updated in real time and they use it to follow their in-wandering warehouse teams, beginning inventory movement, using assets, making faster decisions.
Manual scanning is eliminated and human errors are reduced, which means logistics operations can be done quickly and accurately with the help of RFID.
The Uses of RFID in Logistics
1. Inventory Management
One of the primary applications of RFID in logistics is inventory management. Traditional manual inventory tracking methods are time-consuming and prone to errors. RFID streamlines this process by providing real-time visibility into the movement of goods.
With RFID tags on products, warehouse managers can quickly identify and locate items, reducing the chances of stockouts and overstock situations. This ensures that the right products are in the right place at the right time, optimizing supply chain operations.
2. Asset Tracking
One of the primary roles of RFID usage in warehouses is asset tracking. RFID technology allows for the continuous monitoring of assets, enhancing security and minimizing the risk of theft or misplacement. Real-time asset tracking also enables better resource allocation and improved maintenance scheduling, resulting in cost savings and increased operational efficiency.
3. Order Accuracy
Order fulfillment accuracy is paramount in logistics and warehousing. RFID technology minimizes picking errors by automating the process. When a worker picks an item with an RFID tag, the system verifies that it matches the order, reducing the likelihood of shipping incorrect products to customers. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also saves time and resources by avoiding costly order corrections. This is an important use of RFID in logistics.
4. Warehouse Efficiency
RFID in logistics significantly enhances warehouse efficiency. It enables automated and real-time tracking of goods as they move through the facility. This leads to faster decision-making, reduced search times, and optimized storage space utilization. Warehouse managers can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, allowing for continuous process improvement.
5. Supply Chain Visibility
RFID technology provides unparalleled visibility into the supply chain. From the moment a product is manufactured to its final delivery, RFID tags allow logistics professionals to monitor its journey in real time. This visibility enables proactive problem-solving, timely interventions, and better decision-making, ultimately improving the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
The Advantages of RFID in Logistics Management
RFID warehouse systems play a key role in increasing the efficiency of your supply chain management. Here are a few benefits listed below.
1. Enhanced Accuracy
RFID technology greatly improves data accuracy compared to manual tracking methods. With RFID, the margin for error is significantly reduced, leading to more precise inventory counts, order picking, and asset tracking. This increased accuracy translates into improved customer satisfaction and cost savings.
2. Real-time Monitoring
One of the standout benefits of RFID in logistics is its ability to provide real-time information. Logistics managers can access up-to-the-minute data on inventory levels, asset locations, and shipment statuses. This real-time monitoring allows for quicker decision-making and better responsiveness to changing circumstances in the supply chain.
3. Cost Reduction
RFID technology can lead to substantial cost reductions in logistics and warehousing operations. By automating manual tasks, streamlining processes, and preventing errors, RFID helps reduce labor costs and minimize the expenses associated with order errors and stockouts. Additionally, the improved visibility and tracking of assets contribute to more efficient resource allocation.
4. Increased Productivity
With RFID, the productivity of both workers and equipment is significantly boosted. Employees spend less time searching for items or manually entering data, freeing up their time for more value-added tasks. Forklifts and other equipment can operate more efficiently with RFID guidance systems, reducing the risk of accidents and product damage.
5. Scalability
RFID systems are highly scalable, making them suitable for businesses of all sizes. Whether you run a small warehouse or a large-scale logistics operation, RFID technology can be tailored to your needs. As your business grows, you can easily expand and adapt your RFID infrastructure to accommodate increased volumes and complexities.
Furthermore, let’s quickly get to the frequently asked questions for RFID in logistics and warehouse centers.
Real-World RFID Success Story: Warehouse Makeover
Challenge: A 200,000-square-foot distribution center was battling 15% inventory variation and devoting 40 hours a week to manual counts.
Solution: Deployed UHF RFID system comprising of 12 fixed readers and 4 handheld scanners in receiving, storage and shipping areas.
Results:
- Raised inventory accuracy from 65 to 99.4 %
- Cycle counting time now just 6 hours a week instead of 40
- Accuracy of order fulfillment increased to 99.8%
- ROI in 14 months
- $180,000 per year in labor and errors saved
Conclusion
RFID in logistics and warehousing has become an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to optimize their supply chain operations. From inventory management and asset tracking to order accuracy and cost reduction, RFID technology offers a wide range of uses and benefits.
As technology continues to advance, RFID in logistics will likely play an even more significant role in shaping the future of supply chain management, helping businesses stay competitive in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Do you want to implement RFID in your business? Look no further than Qodenext to achieve accuracy, real-time monitoring, and reduced costs. Aldo read: What are the 5S of Warehouse?
FAQs – RFID in Logistics and Warehouse
1. What is the difference between RFID and barcode technology in logistics?
While both RFID and barcode technologies are used for tracking and identification, they differ in several ways. RFID does not require direct line-of-sight scanning, allowing for faster and more automated data capture.
RFID tags can also store more data than barcodes and are more durable, making them suitable for challenging environments. However, RFID implementation can be more expensive upfront compared to barcodes.
2. Is RFID secure for tracking sensitive information in logistics?
Yes, RFID technology can be secured to protect sensitive information. Advanced encryption and authentication mechanisms can be implemented to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data. Additionally, RFID can provide audit trails and access logs for added security.
3. Can RFID be integrated with existing logistics and warehouse management systems?
Yes, RFID systems can be integrated with existing systems. Many RFID solutions are designed to work seamlessly with common warehouse management and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. This integration allows for a smooth transition to RFID technology without disrupting existing operations.
4. What are the potential challenges of implementing RFID in logistics?
RFID implementation may face challenges such as the initial cost of tags and readers, the need for infrastructure changes, and potential interference from metal or liquids. However, these challenges are often outweighed by the long-term benefits of improved efficiency and accuracy.
5. What is the read range of RFID tags in logistics?
Read range is a function of tag type (passive vs active), frequency (LF, HF, UHF), and environmental conditions (metal, interference). In warehouse applications, passive UHF tags can be read from a few meters to 10+ meters at best, whereas active RFID tags can be read tens of meters or farther. Good coupling, antenna matching and interference reduction are important for good range.
6. How accurate is RFID in inventory – tracking?
From accuracy point of view, the system can be very accurate; in many cases, it can increase accuracy of inventory from 60-70% (manual) to 95%+ if deployed properly. The actual accuracy is dependent on quality of tag, the reader configuration, environmental interference, and the configuration. The results from/promise of accuracy is appropriate for calibration and pilot testing.
7. How accurate can RFID inventory tracking get?
When implemented correctly, RFID systems can enhance inventory accuracy dramatically — on the order of from ~70% (manual methods) accuracy to over 95%+ accuracy. Success depends upon proper tag placement, reader layout, environment (metal/liquid RF interference) and system calibration. The result: Less inventory lost under shop shelves, fewer out of stock / too many in stock situations, and greater responsiveness.
8. Does RFID adoption require a new WMS system?
Not necessarily. Many RFID solutions can be integrated with existing warehouse management systems (WMS) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions. It’s all in the name of compatibility, making sure your middleware, your API links, your data flows, your work flows, all are checked. You can upgrade your system rather than replace it, if you plan properly.







