Businesses today must operate at a fast pace to keep up with the ever-changing demands of the market and their customers. Traditional manufacturing processes, which focus on efficiency and producing uniform products, are no longer well-suited for these new challenges. That’s where agile manufacturing comes in.
Agile manufacturing is a modern approach that emphasizes flexibility, speed, and responsiveness in production. Simply put, Agile Manufacturing = Flexibility + Speed + Responsiveness. This method helps companies stay competitive by allowing them to customize products and quickly adapt to market changes.
In this blog, we will explore what manufacturing agility means, its core principles and methods, the benefits and drawbacks, its real-world applications, and how it connects with lean manufacturing.
What Is Agile Manufacturing?
Agile manufacturing is a style of manufacturing that emphasizes flexibility, customer focus, and quick response. Whereas traditional manufacturing systems stress stability and economies of scale, agile manufacturing meaning that companies can quickly transform themselves to meet new customer needs and market conditions.
It is a term that surfaced out of the need to connect technology innovation and human endowments with responsive methods of effective yet flexible production. With the help of IoT, AI, robotics, and automation, organizations are able to produce quality products and reduce lead times. Companies have to be agile; it is especially important in industries like automotive and electronics or fashion, fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), where customers’ preferences can change weekly if not daily.
Key Principles of Agile Manufacturing
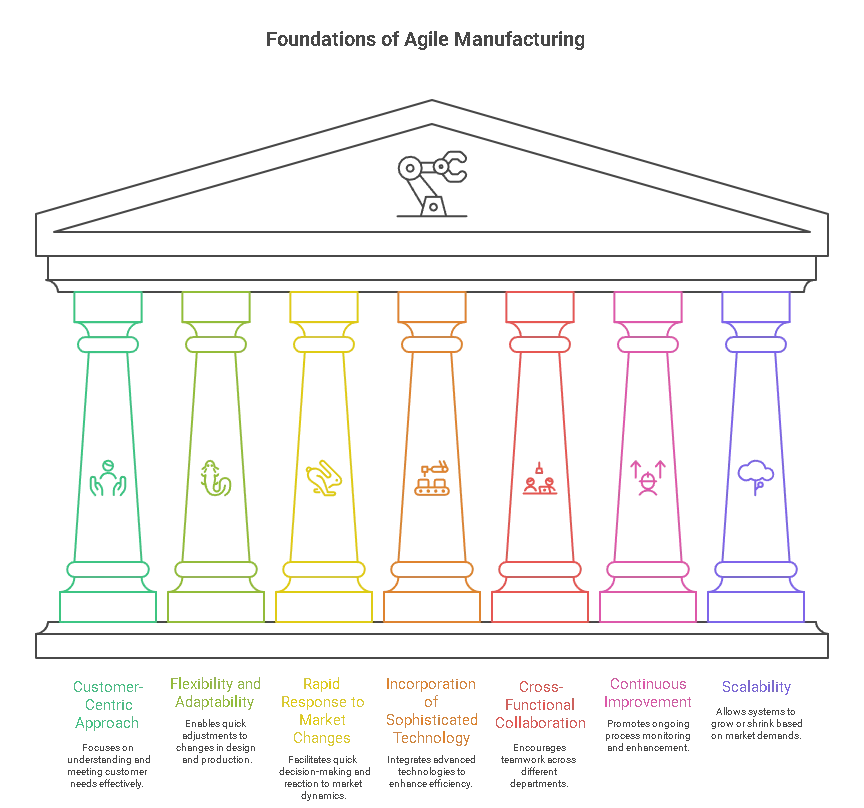
The foundation for the success of agile manufacturing is based upon some key principles:
1. Customer-Centric Approach
Agile manufacturing places the customer at the center of the production process. This is more about understanding the customers’ requirements and responding quickly by modifying the product to meet customer needs.
2. Flexibility and Adaptability
Thanks to modular processes and flexible production systems, companies can easily adapt to changes in design, in production quantity, or in delivery date.
3. Rapid Response to Market Changes
Companies can make decisions faster and with shorter lead times to get in front and react to competitive threats or react quicker to changes in the market.
4. Incorporation of Sophisticated Technology
IoT, AI, robotics, and automation are critical technologies to monitor production, predict demand, and maximize efficiency.
5. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Design, manufacture, supply chain, and marketing teams work together to resolve problems and innovate more quickly.
6. Continuous Improvement
You have to think that-agile manufacturing is fluid Processes are monitored, adapted, and improved continually to enhance efficiency and speed.
7. Scalability
Agile systems can grow or shrink according to the demands of the market or the needs of production, so they can be used by both small and large organizations.
By applying these principles, a company can achieve the speed, quality, and cost combination that the competitive market requires today.
Approaches to Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing is becoming a serious concept of concern to be adopted for successful manufacturing in diverse business environments biased towards adaptable and flexible production systems.
1. Modular Production
In modular production, the whole manufacturing process is divided into relatively small, independent modules. They are simple to rearrange so as to create different products or address variations in the output.
2. Flexible Supply Chains
Agile manufacturing relies on responsive suppliers and logistics partners who can respond rapidly to its changing demand or supply situation.
3. Cross-Functional Teams
Interdisciplinary teams in different units collaborate, eliminating silos within the team.
4. Just-in-Time Production (JIT)
JIT production helps ensure that only the necessary amount of inventory is maintained, and goods are produced when needed, which reduces waste and storage costs.
5. Rapid Prototyping and Testing
Quick-spelling companies design very high-speed prototypes as use tests to assess and, if needed, redesign their product before taking it to mass production.
6. Customer Feedback Integration
There are continuous customer feedback channels in agile manufacturing to improve products, services, and processes.
7. Cloud-Based Production Planning
Utilizing cloud computing for production planning allows an enterprise to monitor the business processes in real-time, collaborate efficiently, and quickly respond to change.
Organizations can also achieve high responsiveness, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction based on the adoption of these strategies.
Agile Manufacturing vs. Lean Manufacturing
Although lean manufacturing and agile manufacturing are both focused on improving production, they do so with different aims:
| Aspect | Lean Manufacturing | Agile Manufacturing |
| Main Focus | Efficiency and waste reduction | Flexibility and responsiveness |
| Process | Standardized and streamlined | Adaptive and modular |
| Inventory Management | Minimal inventory | Flexible inventory |
| Risk Management | Focuses on minimizing risks through elimination of waste and defects | Emphasizes rapid adaptation to uncertainties and market changes |
| Customer Orientation | Indirect focus | Direct, customer-driven |
| Production Speed | Optimized for cost and efficiency | Optimized for fast market response |
| Technology Use | Moderate | High (IoT, AI, automation) |
The majority of contemporary organizations integrate lean and agile manufacturing practices to design a hybrid system that suits their needs for efficiency and flexibility. Understanding the subtle differences between lean manufacturing and agile manufacturing is crucial for successful implementation.
Advantages of Agile Manufacturing
There are a lot of benefits to agile manufacturing, including:
1. Shorter Time to Market
Agile production cycles allow companies to rapidly adapt to shifting trends by achieving higher speeds to market.
2. Higher Customer Satisfaction
Custom products with customers’ specs for a more engaging and tailored user experience.
3. Stronger Competitive Position
Companies are better able to respond to shifts in the market, helping them compete better.
4. Lower Inventory Costs
Flexible production holds less inventory and reduces storage and carrying costs.
5. Enhanced creativity
Rapid prototyping, modular systems, and incremental releases make it possible to develop and innovate products continuously.
6. Scalability
Flexible manufacturing systems can be scaled up or down efficiently with variation in demand.
7. Visibility of Operations
With the state-of-the-art technology, collaboration can be monitored, reported in real-time, and improved by decision-making.
Real-World Examples of Agile Manufacturing
Some examples of top companies that successfully incorporated agile manufacturing include:
• Toyota:
Uses modular production and cross-functional teams to increase efficiency and quickly adapt to change.
• Zara:
Harnesses a fast-fashion model that reacts to consumer trends every week through a quick-response production.
• Cisco:
Practices agility in its electronics manufacturing and is able to adapt quickly to technical changes.
• GE Appliances:
Leverages automation and IoT-based solutions to deliver faster, more flexible production runs.
Challenges of Agile Manufacturing
The benefits of agile manufacturing are many, but so are the challenges:
• High Initial Investment
Advanced technology and trained personnel can be costly in the beginning.
• Complicated Supply Chain Coordination
Coordinating with flexible suppliers and logistics providers is much more challenging than conventional coordination.
• High-Skilled Workforce Needed
Personnel must be trained to rotate among departments and to adapt quickly to new production systems.
• Change Resistance
Resistance can be felt within companies when introducing new processes/best practices or organisation ways of working.
• Achieving a Balance between Flexibility and Costs
Overly flexible systems can increase production costs if not checked.
Steps to Implement Agile Manufacturing
To effectively adopt agile manufacturing, businesses may take the following steps:
1. Begin with a Pilot Project
Pilot your agile approaches rather than going directly to a full company-wide implementation.
2. Train Employees
Build skills for cross-functional teamwork, problem-solving, and technology use.
3. Leverage Technology
Use IoT, AI, robotics, and cloud-based software to enhance real-time monitoring, making proactive decisions.
4. Measure and Analyze
Continuous performance monitoring through KPIs and metrics to identify gaps for improvement.
5. Gradual Scaling
Introduce and scale agile processes within product lines and functions gradually for a smooth changeover.
There is no question that agile manufacturing is a strategic necessity for today’s businesses and not a fad. Through the adoption of flexible and technology-enabled, customer-centric processes, organizations are able to reduce lead times, enhance product customization, and maintain a strong competitive edge.
Solutions for real-world challenges and advice on how to get started with agile, flexible manufacturing strategies are available in Qodenext’s Solutions, Case Studies, and White Papers.
People Also Ask (FAQs)
1. What is the principle of agile manufacturing?
Agile manufacturing focuses on speed, flexibility, and custom-driven production.
2. What companies use agile manufacturing?
Toyota, Zara, Cisco, and GE Appliances are a few.
3. What is the difference between lean and agile manufacturing?
Lean is trying to be efficient, and agile is trying to be flexible and responsive.
4. How does agile manufacturing enhance production?
It reduces lead times, allows customization of products, and responds to market fluctuations.
5. Is agile manufacturing feasible for small businesses?
Yes, adaptable and modular concepts enable its implementation in any size company.
6. How important is technology in agile manufacturing?
Technology enables live monitoring, rapid prototyping, and efficient decision-making.
7. What are the tactics of agile manufacturing?
Modular production, JIT manufacturing, cross-functional teams, flexible supply chains, and rapid prototyping.
8. What are the best features of agility manufacturing?
Delivery is quicker, customer satisfaction has increased, competition is better managed, costs of holding inventory are reduced, and there is more innovation.
9. What could be the company’s problems?
Expensive, complex supply chains, workforce training, and people resisting change.
10. How to Successfully Adopt Agile Manufacturing:
Start small, train teams, adopt technology, track progress, and scale processes incrementally.






