For decades, asset management in India relied on fragmented processes, including manual audits, visual inspections, and barcode-based tracking. While barcoding brought structure, it still required line-of-sight scanning and was prone to errors. As industries expanded and supply chains grew global, these systems could not provide real-time asset visibility or scalability.
UPI, digital payment gateways and other initiatives like Digital India, affordable connectivity, and the push for Industry 4.0 adoption created the perfect environment for IoT and RFID integration. These technologies are now helping businesses manage everything from raw materials to finished goods, machinery, tools, vehicles, and even returnable transport items.
How IoT and RFID Transform Asset Management
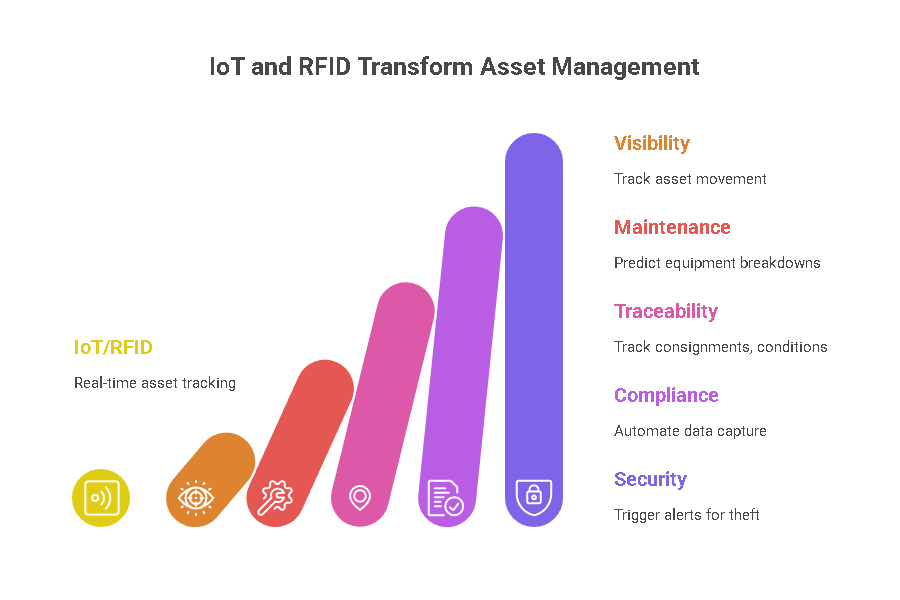
Here are the various ways smart connectivity devices are helping in asset tracking:
1. Real-Time Asset Visibility
IoT sensors combined with RFID tags enable enterprises to track asset movement across warehouses, shop floors, and distribution channels in real time. This eliminates guesswork, reduces asset misplacement, and helps businesses make informed decisions instantly. For example, an IoT warehouse inventory facility in India can monitor stock levels at multiple depots and trigger automatic replenishments.
2. Predictive Maintenance of Equipment
Heavy industries, utilities, and transport companies in India face frequent downtime due to reactive maintenance. IoT and RFID provide a smarter approach: sensors track usage, temperature, vibration, and wear-and-tear, allowing predictive analytics to alert managers before breakdowns occur. Think smart maintenance in near-perfect time.
3. Supply Chain Traceability
India’s logistics ecosystem is vast, with multi-modal networks stretching from ports to rural towns. By integrating IoT and RFID real-time analytics, companies track consignments, monitor environmental conditions such as temperature or humidity, and ensure compliance with quality standards. This is particularly critical for sectors like pharmaceuticals and food, where product safety is necessary.
4. Automated Compliance and Auditing
Audits in traditional systems were labour-intensive and error-prone. With IoT and RFID asset management, compliance data (such as asset usage logs, movement history, and calibration records) is automatically captured, time-stamped, and stored. This ensures seamless regulatory audits, especially in sectors governed by strict standards like aviation, oil and gas, and healthcare.
5. Enhancing Security and Loss Prevention
Despite significant progress, theft, loss of goods, and business malpractices continue to pose substantial challenges in the logistics and retail industries. RFID tags integrated with IoT-enabled geofencing can trigger alerts if assets move out of designated zones. For high-value assets, real-time notifications allow immediate interventions, significantly reducing losses.
IoT and RFID and India: Asset Management
Indian brands are poised to take charge of the connectivity industry. Here’s why:
• Scale and Diversity:
With one of the largest supply chain ecosystems in the world, India needs scalable solutions to track billions of assets across urban and rural landscapes.
• Regulatory Push:
Government initiatives such as GS1 India for supply chain standards and mandatory RFID toll collection via FASTag show institutional support for RFID adoption.
• Affordability of Technology:
Falling costs of RFID tags (as low as ₹5–₹10 per tag in bulk) and IoT devices make deployment feasible even for SMEs.
• Digital Ecosystem:
India’s robust 4G/5G rollout and cloud adoption enable seamless connectivity, essential for IoT and RFID systems to function efficiently. This increases the need for IoT tracking systems.
Real-Life Examples from Indian Industries
Many indian firms are rapidly integrating tracking tools to eliminate structural bottlenecks. Here are a few examples:
• Healthcare –
Apollo Hospitals: RFID-enabled patient wristbands and equipment tracking cut administrative errors and improved patient safety. IoT sensors track sensitive medicines across administrative checkpoints, ensuring proper shelf life and compliance audits.
• Railways –
Indian Railways: Over 3 lakh freight wagons and 30,000 locomotives are being fitted with RFID tags to track movement and plan predictive maintenance, reducing delays and operational costs.
• Logistics –
Flipkart & Amazon: RFID-powered scanning in warehouses enables near-instant inventory checks. IoT sensors ensure temperature-sensitive shipments like vaccines stay within safe ranges.
• Retail –
Shoppers Stop: They have implemented a landmark RFID tagging project to reduce shoplifting burden and increase staff efficiency. The result was faster billing and higher inventory accuracy.
• Infrastructure –
Delhi Metro: Uses IoT-enabled sensors to monitor escalators, elevators, and critical equipment, preventing downtime and enhancing passenger safety.
• Manufacturing –
Tata Motors: Employs RFID and IoT sensors to track parts across assembly lines, ensuring just-in-time availability and preventing costly stoppages.
RFID Inventory Tracking in India: Challenges to Overcome
While adoption is accelerating, Indian enterprises must navigate certain hurdles:
• High Initial Investments:
Though long-term ROI is strong, upfront costs of infrastructure, readers, and integration deter some businesses.
• Interoperability Issues:
Legacy ERP systems may not integrate smoothly with IoT platforms.
• Skill Gaps:
Organisations need skilled professionals to manage and interpret IoT data effectively.
• Data Privacy Concerns:
With sensitive operational data flowing across connected devices, cybersecurity and compliance must be prioritised.
The Road Ahead: IoT and RFID in India
The future of asset management in India will be defined by IoT and RFID convergence with other advanced technologies:
• AI and Analytics:
Predictive models powered by AI will turn raw IoT data into actionable insights.
• Blockchain Integration:
Combining blockchain with RFID will create tamper-proof records, ensuring authenticity in sectors like pharmaceuticals and luxury goods.
• 5G Acceleration:
Ultra-low latency networks will make real-time monitoring seamless, even in remote areas.
• Sustainable Operations:
IoT-enabled energy meters and RFID-driven reuse of returnable assets will help companies align with ESG goals.
With increasing competition and regulatory scrutiny, asset-intensive industries cannot afford inefficiency. As adoption deepens, IoT and RFID will shift from being optional add-ons to foundational components of business strategy in India.
Conclusion
The adoption of IoT and RFID in India represents more than just a technological upgrade; it’s a fundamental shift in how businesses perceive and manage assets. By offering real-time visibility, predictive maintenance, compliance automation, and theft prevention, these technologies are enhancing speed, efficiency, and agility.
As connectivity expands and costs continue to drop, these tools will not only help Indian businesses achieve efficiency but also make them globally competitive. Ready to explore logistics tracking in real-time? Contact Qodenext today.
FAQs – IoT and RFID
1. What is the difference between IoT and radio-frequency devices in asset management?
RFID is primarily used for identification and tracking through tags and readers, while IoT combines sensors, connectivity, and analytics to monitor asset condition, usage, and performance. Together, they deliver end-to-end visibility.
2. How are Indian SMEs benefiting from connectivity technologies?
SMEs in sectors like textiles, retail, and logistics are using affordable RFID tagging and IoT dashboards to reduce pilferage, automate stock management, and improve delivery accuracy—all at lower operational costs.
3. Are IoT and smart solutions expensive to implement in India?
Costs have fallen significantly in recent years. Basic RFID tags are inexpensive, and cloud-based IoT platforms eliminate the need for heavy IT infrastructure. While there is an upfront investment, the long-term savings on labour, losses, and downtime outweigh the costs.
4. What role does the Indian government play in promoting smart network systems?
Government projects like FASTag for toll collection, GS1 India for supply chain standards, and the Smart Cities Mission highlight institutional endorsement of these technologies.
5. Which industries in India will see the fastest adoption of IoT, Mobile-To-Mobile connectivity, and RFID?
Logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing are leading the way, but retail, agriculture, and energy sectors are also catching up quickly as solutions become more affordable.