When you pick up your phone, drive your car, or even open a pack of chips, you rarely think about how many checks and inspections those products went through before reaching you.
Yet, manufacturing quality control is what stands between a flawless product and one that could damage a company’s reputation overnight.
Traditionally, human inspectors handled most of this work. They look for scratches, misalignments, or defects on production lines. But there’s a problem. Humans get tired, make mistakes, and can’t possibly check thousands of items per minute.
That’s where Machine Vision is stepping in, changing the game entirely.
Now let’s dive into what this technology really is, and why it’s becoming the backbone of modern factories.
What Is Machine Vision?
At its simplest, Machine Vision is like giving “eyes” to machines. Cameras, sensors, and algorithms work together to capture images of products and analyze them in real-time.
But it’s not just about taking pictures. It’s about:
- Detecting flaws that even a trained human eye might miss
- Measuring accuracy (e.g., is a car part exactly 3.2 mm wide?)
- Tracking items as they move across a production line
- Making instant decisions (pass, fail, or rework)
In short, machine vision quality control is about bringing precision, speed, and consistency to manufacturing processes.
Now that we know what machine vision is, let’s explore why it matters so much in quality control.
Why Machine Vision Matters in Quality Control
Manufacturers face a constant balancing act: produce faster, reduce costs, and maintain perfect quality. Relying on humans alone makes this almost impossible. Machine vision systems manufacturing ensures quality is not left to guesswork.
Here’s what makes it essential:
• Zero fatigue –
Unlike humans, machines don’t lose focus.
• Microscopic accuracy –
Catching defects invisible to the naked eye.
• Speed –
Inspecting thousands of units per minute.
• Traceability –
Logging every inspection for compliance and audits.
For example, in the automotive industry, BMW uses machine vision quality control to inspect weld seams on car bodies. One missed defect could mean recalls worth millions, so relying on cameras and algorithms ensures no error slips through.
Now that we’ve seen why machine vision is important, let’s dig into how it’s actually applied on factory floors.
Real-World Applications of Machine Vision in Manufacturing
Industrial machine vision applications aren’t limited to one sector – they’re everywhere. Let’s break it down with some real use cases:
1. Electronics Industry
- Checking solder joints on circuit boards
- Verifying component placement
- Example: Intel uses machine vision systems manufacturing to ensure chips are defect-free before packaging.
2. Food & Beverage Industry
- Detecting foreign particles in packaged foods
- Checking if labels are correctly placed
- Example: Coca-Cola uses machine vision quality control to confirm every bottle has the right fill level and cap seal.
3. Pharmaceuticals
- Verifying pill shapes, sizes, and packaging integrity
- Ensuring barcodes are readable for traceability
- Example: Pfizer relies on manufacturing automation quality control to prevent dosage errors and ensure patient safety.
4. Automotive Industry
- Inspecting paint finishes for scratches or bubbles
- Measuring dimensions of critical parts
- Example: Tesla uses machine vision for real-time quality monitoring on its Gigafactory assembly lines.
These examples show how powerful and diverse the technology is. But what about the systems behind it?
Inside a Machine Vision System: How It Works
A typical machine vision system has several components working in harmony:
| Component | Role in Quality Control |
| Cameras & Sensors | Capture high-resolution images of products |
| Lighting Systems | Highlight defects, shadows, or surface irregularities |
| Processing Units | Run algorithms to analyze images |
| Software | Decides whether a product passes or fails |
For instance, on a car assembly line, a camera may capture an image of a door. The system instantly compares it to the “perfect” model. If there’s a 1mm gap misalignment, the system flags it, ensuring it’s fixed before moving forward.
Now that we’ve unpacked how machine vision systems work, let’s look at how they’re shaping the bigger picture – automation in manufacturing.
Machine Vision as the Backbone of Manufacturing Automation
Automation isn’t just about robots replacing human workers – it’s about making smarter, faster, and safer production lines. Manufacturing automation quality control powered by machine vision ensures that automation doesn’t compromise quality.
Key roles include:
- Guiding robots to assemble parts with surgical precision
- Monitoring packaging lines at lightning speed
- Reducing waste by spotting errors before they multiply
- Supporting sustainability goals by ensuring fewer defective products reach customers
Amazon warehouses, for example, use industrial machine vision applications to help robots identify packages, sort them accurately, and ensure quality standards are never compromised, even during peak demand seasons.
Now that we’ve seen how it drives automation, let’s talk about the benefits companies are actually experiencing.
Benefits of Machine Vision Quality Control
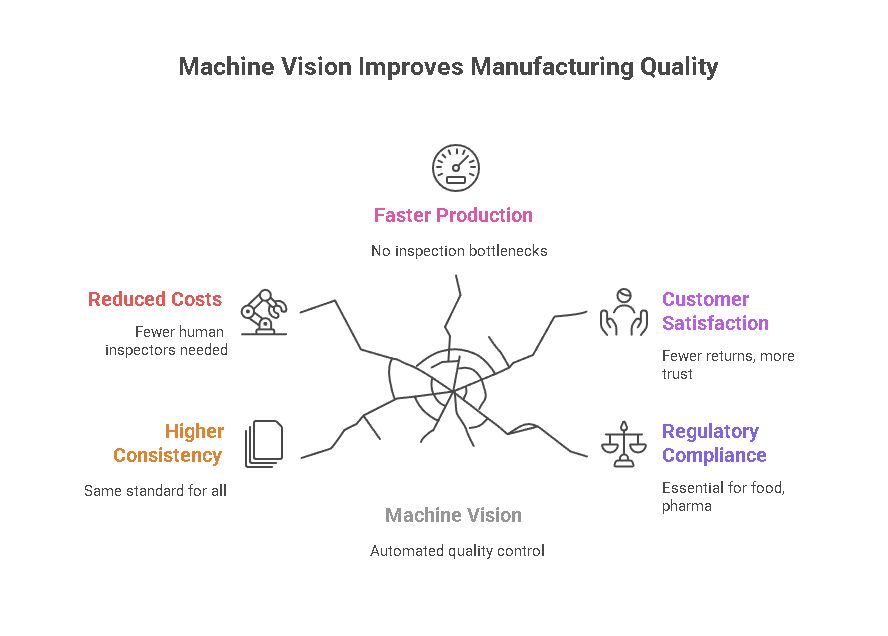
The adoption of machine vision quality control isn’t just about fewer defects—it’s about transforming the entire manufacturing workflow. Some of the biggest benefits include:
• Higher consistency –
Every product is judged by the same standard
• Reduced labor costs –
Eewer human inspectors required
• Faster production cycles –
No bottlenecks in inspection stages
• Better customer satisfaction –
Fewer returns, more trust
• Regulatory compliance –
Essential in industries like food and pharma
When you add these up, it’s easy to see why industries are racing to adopt machine vision systems manufacturing as a core part of their operations.
Challenges and Considerations
Of course, no technology is without hurdles. Adopting machine vision quality control comes with:
- High upfront costs for hardware and software
- Integration issues with older production lines
- Training needs for staff to manage new systems
- Data overload if not handled properly
But here’s the flip side: companies that invest in these systems often see a rapid return, as fewer defects mean less waste and higher profits.
Now that we’ve looked at challenges, let’s wrap it up with the bigger picture – where this technology is heading.
The Future of Machine Vision in Manufacturing
The next wave of industrial machine vision applications will go beyond just spotting defects. With the integration of AI and IoT, machine vision will:
- Predict failures before they happen (predictive maintenance)
- Enable “lights-out factories” that run with minimal human input
- Personalize products at scale by adjusting in real-time
- Strengthen sustainability through smarter material use
Imagine a factory where products are designed, inspected, and shipped with almost no human intervention – this is the future many manufacturers are already testing.
Conclusion
In today’s hyper-competitive landscape, there’s no room for errors. Machine vision quality control isn’t just another tool- it’s a necessity for survival. From Coca-Cola’s bottling lines to Tesla’s gigafactories, machine vision systems manufacturing is proving that better vision equals better quality.
As manufacturing automation quality control continues to evolve, the companies embracing it today will be the ones setting tomorrow’s standards.
FAQs: Why Machine Vision is the Secret to Flawless Quality in Factories
1. What industries benefit most from machine vision?
While it’s used everywhere, industries like automotive, electronics, food & beverage, and pharmaceuticals see the most value from industrial machine vision applications.
2. How does machine vision differ from AI in quality control?
Machine vision captures and analyzes images, while AI adds the “intelligence” to make predictions, learn patterns, and improve decisions over time.
3. Can small manufacturers adopt machine vision?
Yes. With affordable sensors and cloud-based processing, even small businesses can use machine vision quality control without massive investments.
4. What’s the ROI on machine vision systems?
Most companies see ROI within 1–3 years due to reduced waste, fewer recalls, and faster production cycles.
5. Is machine vision replacing human workers?
Not entirely. It’s more about shifting human roles from repetitive inspection tasks to higher-value problem-solving and system management.