Fulfillment is a crucial part of any business that deals with physical goods. Whether you’re a manufacturer, wholesaler, or retailer, choosing the right fulfillment model can make a significant impact on your operations, costs, and customer satisfaction. Businesses typically fall into two broad categories—B2B (Business-to-Business) and B2C (Business-to-Consumer) fulfillment. Each of these models has distinct operational requirements, challenges, and benefits.
In this blog, we will explore the differences between B2B and B2C fulfillment, their key components, and how to choose the right one for your business.
Understanding B2B and B2C Fulfilment
Before diving into the comparison, let’s define each model:
- B2B Fulfilment: This refers to the process of fulfilling orders from one business to another. Examples include wholesalers supplying retailers, manufacturers shipping bulk goods to distributors, or suppliers providing products to corporate clients.
- B2C Fulfilment: This involves fulfilling orders directly to individual customers. Examples include eCommerce stores, retail brands, and subscription box companies delivering products to end consumers.
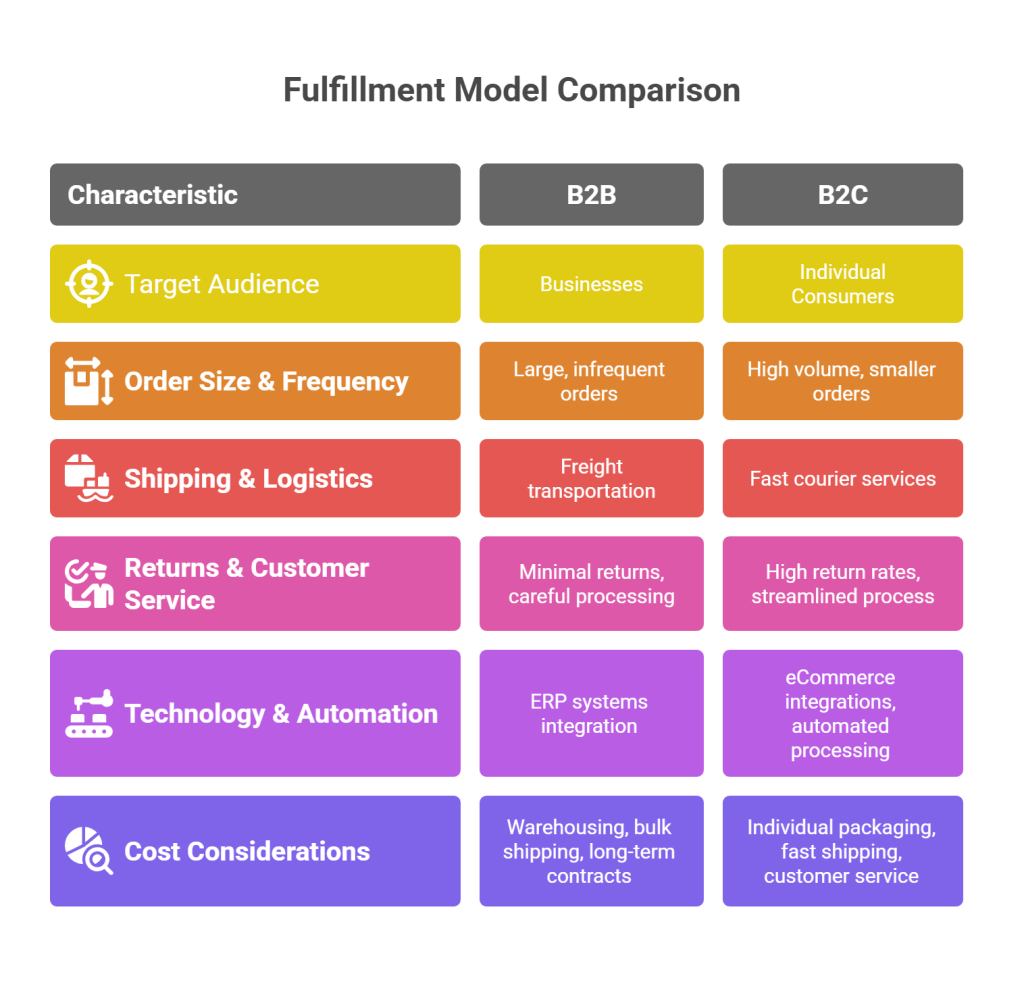
| Aspect | B2B Fulfilment | B2C Mode |
| Order Volume | Large bulk orders | Smaller, individual orders |
| Order Frequency | Less frequent but larger | High frequency with smaller quantities |
| Shipping Requirements | Palletised or freight shipments | Direct-to-consumer shipping, often via courier |
| Lead Time | Longer lead times | Shorter lead times (often same-day or next-day shipping) |
| Packaging | Minimalistic, functional (bulk shipments) | Branded, customer-friendly packaging |
| Returns Management | Less frequent but complex returns process | Frequent and streamlined return process |
B2B Fulfilment: Key Components & Challenges
B2B fulfilment is a complex process that involves handling bulk orders, strict compliance regulations, and coordinated logistics. Here are its major components:
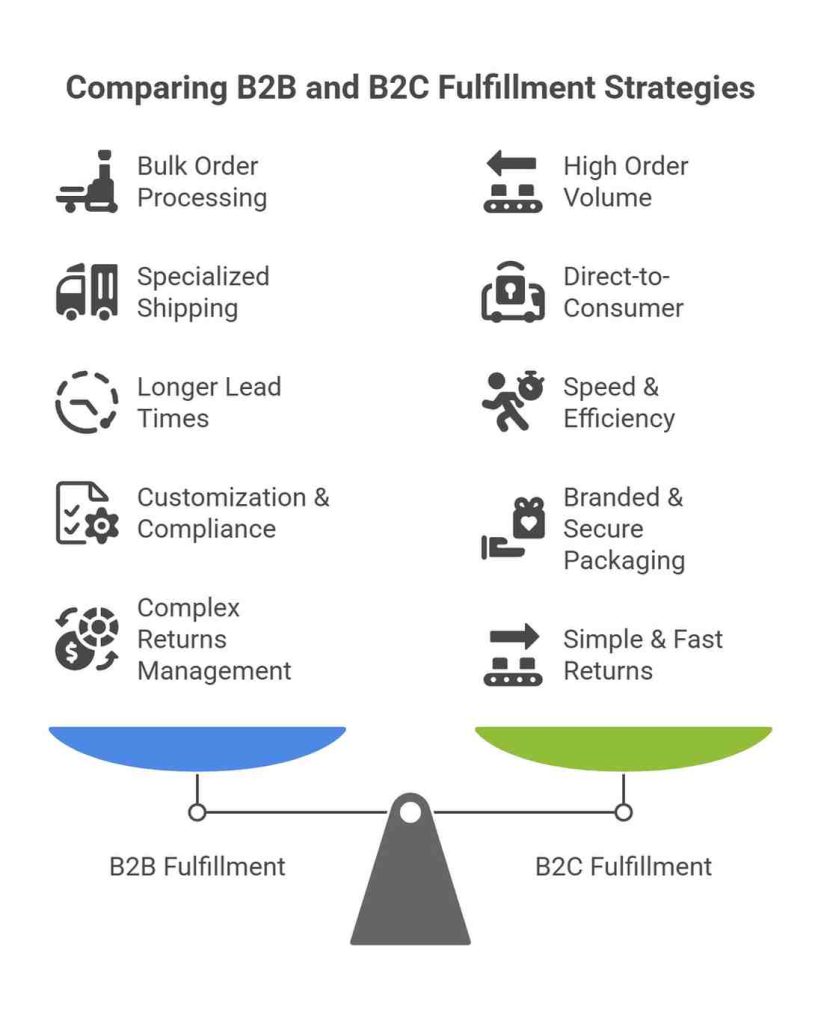
1. Bulk Order Processing
B2B delivery transactions often involve large volumes of goods. Orders may be packed in pallets, crates, or large cartons and require specialized handling equipment like forklifts.
2. Customization and Compliance
Businesses may have specific packaging types, labeling, and compliance requirements. For example, pharmaceutical or food industry suppliers must meet stringent regulatory standards.
3. Longer Lead Times
Unlike B2C fulfillment, where customers expect fast shipping, B2B logistics require longer lead times for production, order assembly, and transportation.
4. Specialized Shipping & Logistics
B2B shipping often involves freight carriers, LTL (Less Than Truckload) or FTL (Full Truckload) shipments, and warehouse-to-warehouse deliveries.
5. Order Accuracy & Relationship Management
Since B2B orders are large and high-value, businesses must maintain high order accuracy. Errors in order fulfillment can result in business contract losses.
Challenges in B2B Fulfillment
- Managing complex shipping logistics
- Handling bulk inventory storage efficiently
- Maintaining compliance with industry regulations
- Managing payment terms and contracts
- Reducing returns management is complicated.
B2C Logistics: Key Components & Challenges
B2C fulfillment prioritises speed, customer satisfaction, and efficiency in handling large numbers of small orders. Here are its major components:
1. High Order Volume & Small Shipments
Unlike B2B, where bulk shipments are common, B2C fulfillment handles many small individual orders daily, often shipped to different addresses.
2. Speed & Efficiency
Customers expect quick delivery (same-day, next-day, or two-day shipping). Businesses must integrate automated warehousing and order processing systems to maintain efficiency.
3. Branded & Secure Packaging
B2C packaging often includes branding, gift-wrapping options, and protective elements to enhance the customer experience.
4. Direct-to-Consumer Shipping
Unlike B2B supply chains, B2C delivery models use couriers (FedEx, UPS, DHL) and last-mile services for quick order fulfillment.
5. Simple & Fast Returns Process
Returns and refunds are common in B2C, requiring businesses to have efficient reverse logistics and customer-friendly policies.
Challenges in B2C Last-Mile Model
- Managing high-order volumes with speed
- Handling Ecommerce returns efficiently
- Managing peak season fluctuations (e.g., Black Friday, holiday sales)
- Controlling shipping costs
How to Choose the Right Fulfilment Model for Your Business
1. Understand Your Target Audience
If your business primarily serves other businesses (wholesalers, distributors, manufacturers), B2B fulfilment is the right choice.
If you sell directly to individual consumers, B2C orders are more suitable.
2. Analyze Order Size & Frequency
- If you deal with large, bulk orders with infrequent transactions, B2B is the better fit.
- If your business relies on a high volume of smaller orders, B2C is ideal.
3. Consider Your Shipping & Logistics Needs
- If your shipments require freight transportation, B2B is necessary.
- If your fulfilment depends on fast courier services, B2C is a better option.
4. Assess Your Return & Customer Service Strategy
- If returns are minimal but require careful processing, B2B is preferable.
- If you anticipate high return rates, having a streamlined B2C returns process is crucial.
5. Evaluate Technology & Automation Requirements
- B2B fulfilment often integrates with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems for large-scale inventory management.
- B2C orders require advanced eCommerce integrations and automated order processing.
6. Cost Considerations
- B2B fulfilment requires investment in warehousing, bulk shipping, and long-term contracts.
- B2C orders involve higher costs related to individual packaging, fast shipping, and customer service.
Hybrid Fulfillment: Best of Both Worlds
Many businesses today cater to both B2B and B2C markets. A hybrid fulfillment strategy can help balance both fulfilment models. For example, a manufacturer may sell wholesale to retailers (B2B) and also offer direct-to-consumer products through an eCommerce store (B2C).
A brand with both retail distribution (B2B) and online D2C sales (B2C) may use a 3PL (Third-Party Logistics) provider to manage both.
Conclusion
Choosing between B2B and B2C fulfilment depends on your business model, target audience, shipping needs, and cost considerations. While B2B fulfilment focuses on bulk efficiency and compliance, B2C prioritises speed and customer experience. Understanding these differences will help you make the right decision to optimise your supply chain and maximise customer satisfaction.
By analysing your order size, delivery expectations, and operational capabilities, you can select the best fulfillment model—or even a hybrid approach—to scale your business successfully. For more assistance in logistics traceability, contact Qodenext today.
FAQs – B2B and B2C Fulfilment
1. What are B2B and B2C orders? Can a business use both?
B2B is business-to-business and B2C is business-to-consumer. Companies can operate both B2B and B2C fulfillment models if they have the right infrastructure, logistics, and inventory management systems in place.
2. Which fulfilment method is more cost-effective?
It depends on your business model. B2B fulfillment is cost-effective for bulk transactions but requires larger storage and logistics investments. B2C fulfillment has higher per-order shipping and packaging costs.
3. How do B2B and B2C fulfilment impact inventory management?
B2B fulfillment requires bulk inventory storage and just-in-time logistics. B2C fulfillment demands real-time inventory tracking due to frequent order fluctuations.
4. What role does technology play in fulfilment?
Both fulfillment models require Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Order Management Systems (OMS), and ERP integrations to optimize efficiency and accuracy.
5. Should I outsource fulfilment or keep it in-house?
If your business processes a high volume of orders, outsourcing to a 3PL provider can improve efficiency. In-house fulfillment works well for businesses with specialized logistics needs.
6. Can a business use both B2B and B2C fulfillment models simultaneously?
Yes, many businesses operate using a hybrid model that combines B2B and B2C fulfillment. This approach allows companies to serve wholesale clients while also directly selling to consumers. Efficient management requires robust inventory systems, flexible logistics, and sometimes partnering with third-party logistics (3PL) providers capable of handling both models seamlessly.
7. How does returns management differ between B2B and B2C fulfillment?
Returns in B2B fulfillment are typically less frequent but can be more complex, often involving bulk goods and specialized compliance. In contrast, B2C returns occur more frequently and require streamlined reverse logistics processes to handle individual customer requests promptly, maintain customer satisfaction, and manage costs effectively.
8. What are some common challenges faced in last-mile delivery for B2C fulfillment?
Last-mile delivery in B2C fulfillment is challenged by high order volumes, diverse delivery locations, and stringent customer expectations for fast shipping. Managing peak seasons, controlling shipping costs, and ensuring real-time tracking while preventing damage during transit are also major concerns that require technology and efficient logistics planning.
9. How important is packaging in differentiating B2B and B2C fulfillment?
Packaging in B2C fulfillment plays a critical role in branding and customer experience, often featuring branded designs, protective materials, and gift-ready options. In B2B fulfillment, packaging is usually minimalistic and functional, focusing on efficiency, bulk handling, and meeting regulatory requirements rather than aesthetics.
10. What key performance metrics should businesses track to optimize B2B and B2C fulfillment?
For B2B fulfillment, key metrics include order accuracy, on-time delivery rates, and compliance adherence. In B2C fulfillment, metrics such as order processing speed, customer satisfaction scores, return rates, and last-mile delivery performance are vital. Tracking these helps refine processes, reduce costs, and improve overall supply chain effectiveness.






