Safety stock plays a pivotal role in inventory management. It buffers against uncertainties such as demand fluctuations, lead time variations, and supply chain disruptions. Without it, businesses risk stockouts, lost sales, and customer dissatisfaction.
In this blog, we’ll explore the best methods for calculating stock, ensuring optimal inventory management and seamless operations.

What Is Safety Stock?
Buffer stock is the additional inventory kept on hand to prevent stockouts caused by unexpected demand spikes or supply delays. It is your business’s safety net, ensuring uninterrupted operations and customer satisfaction.
Why Is Safe Stock Important?
- Prevents Stockouts: Ensures you can meet unexpected demand.
- Reduces Lead Time Risks: Mitigates issues due to supplier delays.
- Improves Customer Satisfaction: Keeps orders fulfilled even in unpredictable situations.
- Supports Seasonal Demand: Handles surges during peak seasons.
To achieve these benefits, calculating stock accurately is crucial.
7 Best Methods to Calculate Stock
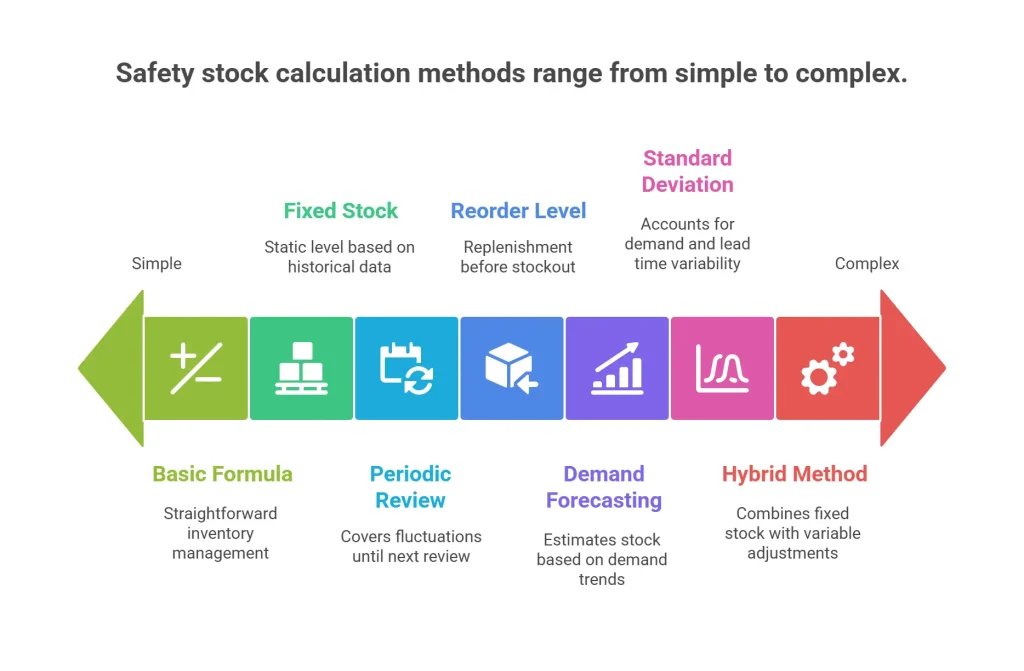
Here’s how to calculate safety stock:
1. Basic Safety Stock Formula
This simple method is widely used for straightforward inventory management needs.
Formula:
Backup Stock = ( Maximum Daily Usage × Maximum Lead Time) − ( Average Daily Usage × Average Lead Time)
Example:
Maximum daily usage: 100 units
Maximum lead time: 10 days
Average daily usage: 80 units
Average lead time: 8 days
Backup Stock
= (100×10)−(80×8)=1000−640=360
This means you should maintain 360 units as safe stock.
2. Standard Deviation Method
This method accounts for demand and lead time variability, making it ideal for businesses with unpredictable trends.
Formula:
Stock = Z×(σD2×Lead Time)+(σLT2×Demand)
Where:
Z: Service level factor (e.g., 1.28 for 90% service level)
σD: Demand standard deviation
σLT: Lead time standard deviation
Example:
- Service level: 90% (Z =1.28)
- σD=50, σLT=3
- Lead time: 10 days
- Daily demand: 100 units
Stock = 1.28×(502×10)+(32×100)=1.28×25000+900=1.28×159.37= 204
Here, 204 units would be your surplus stock.
3. Fixed Safe Stock
A fixed quantity is predetermined based on historical data or business strategy.
How It Works:
Businesses analyze past sales data and industry trends to decide on a static contingency stock level. For instance, if seasonal demand surges lead to stockouts, keeping a fixed stock of 500 units during peak periods could suffice.
Pros:
- Simple to implement.
- Reduces computational needs.
Cons:
This may lead to overstocking or understocking if demand fluctuates widely.
4. Periodic Review Method
In this approach, the stock is calculated to cover fluctuations until the next review period.
Formula:
Surplus Stock = Demand Variability During Lead Time + Review Period
Example:
- Average weekly demand: 1000 units
- The standard deviation of demand: 150 units
- Lead time: 2 weeks
- Review period: 1 week
Safety Stock = 150 × 2 + 1
= 150 × 3 = 260
This method is ideal for companies operating on periodic inventory reviews.
5. Demand Forecasting Method
Using predictive analytics, this method estimates stock based on forecasted demand trends and potential deviations.
Steps to Implement:
- Gather historical data on demand and lead time.
- Use demand forecasting tools (e.g., moving averages or exponential smoothing).
- Calculate deviations and determine the stock accordingly.
Example:
If the forecasted demand for the next quarter is 5000 units with a 10% deviation, maintain 500 units as surplus.
6. Safety Stock and Reorder Level
The reorder point ensures inventory replenishment before a stockout.
Formula:
Reorder Point = ( Average Demand × Lead Time ) + Stock
Example:
Average daily demand: 200 units
Lead time: 5 days
Stock: 300 units
Reorder Point = ( 200 × 5 ) + 300 = 1000 + 300 = 1300
Place a new order when stock reaches 1300 units to prevent shortages.
7. Hybrid Method
Combining multiple approaches, the hybrid method uses fixed buffer stock during predictable periods and adjusts for variability during uncertain times.
How It Works:
- Use fixed stock during stable periods.
- Apply standard deviation or demand forecasting during volatile periods.
- This ensures flexibility and precision in maintaining inventory levels.
Now, that you understand the annual safety stock holding cost formula, let’s explore the crucial factors to calculate inventory levels.
Factors Influencing Stock Calculation
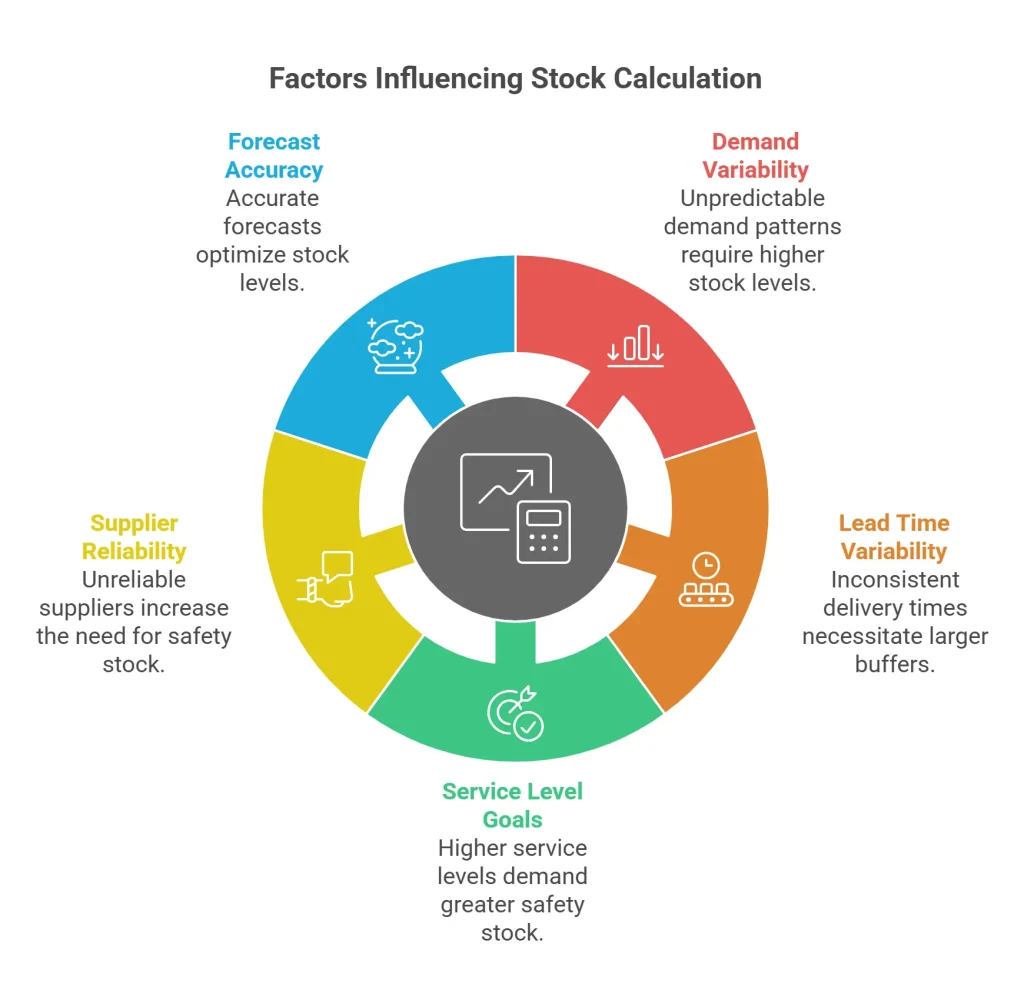
The calculation of stock depends on several critical factors that directly impact a business’s ability to meet demand while avoiding overstocking. Below, we explore these factors in greater detail:
1. Demand Variability
One of the most significant factors affecting safety stock is the variability in customer demand. If demand patterns are unpredictable or seasonal, businesses need higher stock levels to accommodate sudden surges.
2. Lead Time and Its Variability
The lead time—the period between placing an order and receiving it—plays a critical role in determining safety stock. Longer or more inconsistent lead times require higher buffers to prevent stockouts. For example:
- Consistent lead times: A supplier delivering within 3 days consistently may require lower stock.
- Variable lead times: If lead times range from 5 to 15 days, businesses must plan for the longest delays.
- Regularly monitoring supplier performance and exploring backup vendors can help reduce lead time variability and optimize stock levels.
3. Service Level Goals
Your service level is the probability of meeting customer demand without facing a stockout. The higher the service level, the greater the safety stock required. Commonly used service levels include:
- 90% Service Level: Balances inventory costs and availability, suitable for cost-conscious businesses.
- 99% Service Level: This ensures near-perfect availability, which is often necessary in industries like healthcare or aerospace, where stockouts have severe consequences.
Choosing an appropriate service level depends on your industry, customer expectations, and cost tolerance.
4. Supplier Reliability
The reliability of suppliers can significantly impact the amount of safety stock required. If your supplier frequently misses deadlines or ships incomplete orders, maintaining higher stock becomes essential to prevent disruptions.
5. Forecast Accuracy
Accurate demand forecasting is vital to optimizing surplus stock. Poor forecasts can lead to either excessive inventory or insufficient stock levels.
Conclusion
Safety stock is an indispensable part of inventory management, bridging the gap between demand and supply uncertainties. Whether you prefer simple methods like the basic formula or advanced techniques like demand forecasting, the key is to tailor your approach to your business needs. Are you looking for personalized supply chain guidance? Look no further than Qodenext to elevate your logistics operations.
FAQs – Safety Stock
1. What is surplus stock, and why is it important?
Surplus stock is extra inventory maintained to prevent stockouts during demand surges or supply delays. It ensures customer satisfaction and smooth operations.
2. How do I choose the best method for calculating safe stock?
The choice depends on your business needs, demand patterns, and inventory complexity. Use simple formulas for predictable demand and advanced methods for variability.
3. What is the role of service level in stock calculation?
Service level defines the probability of avoiding a stockout. Higher service levels require more stock to cover uncertainties.
4. Can surplus stock lead to overstocking?
Yes, if calculated incorrectly or based on outdated data, surplus stock may lead to excessive inventory and increased holding costs.
5. How often should I review stock levels?
Review stock regularly, especially during demand shifts, supplier changes, or market fluctuations, to ensure accuracy.
6. How does supplier reliability affect safety stock levels?
Supplier reliability directly impacts how much safety stock you should hold. If your suppliers consistently deliver on time and in full, you can reduce your buffer stock. However, if there are frequent delays or incomplete shipments, maintaining a higher level of safety stock helps mitigate those risks and keeps your operations running smoothly.
7. How can forecast accuracy improve safety stock management?
Accurate forecasting allows you to tailor safety stock precisely to expected demand, lowering costs associated with excess inventory while preventing stockouts. Poor forecasts, on the other hand, can either leave you understocked—with lost sales—or overstocked, increasing holding costs.
8. What role does lead time variability play in determining safety stock?
Variability in lead time increases uncertainty, which means you need more safety stock to cover potential delays. If supplier lead times fluctuate greatly, your buffer stock should be sized to handle the longest expected delay to avoid running out during unexpected wait times.
9. How often should businesses review and adjust their safety stock levels?
Safety stock should be reviewed regularly, especially when there are changes in demand patterns, supplier performance, or lead times. Regular reviews ensure that your safety stock reflects current market realities and operational needs, preventing both shortages and excess inventory.
10. Can technology help optimize safety stock calculations?
Yes, many modern inventory management systems incorporate advanced analytics, demand forecasting, and real-time data monitoring to calculate optimal safety stock levels dynamically. This technology helps businesses respond faster to changes in demand or supply and maintain lean, efficient inventory without risking stockouts.






