
The journey of each product that we use today, starts with an idea and the acquisition of raw materials. It then goes through various stages before finally landing in the hands of the consumer. You can trace your products and see how it has evolved into a usable experience for customers.
Each product also goes through testing before being launched and after the users experience them, then manufacturers make adjustments to keep up with the evolving customer demands.
However, the most important part of the product journey is the raw materials. We’ll see what raw material is, its types and how it affects the supply chain of product manufacturing.
What is Raw Materials?
Raw materials are minimally processed items that serve as the fundamental components manufacturers need for the production of goods and services. These materials govern how the products travel throughout the supply chain.
You can divide these materials into various categories, depending on their source and their manufacturing process. Let’s see a few of them:
Types of Raw Materials
You can categorise these components based on their origin:
- Plant/Tree-Based: Includes materials like flowers, fruits, vegetables, wood, resin and latex.
- Animal-Based: Includes materials like leather, meat, bones, milk, wool and silk
- Mining-Based: Includes materials like minerals, metals, crude oil and coal extracted from earth.
While the above types depend on the primary commodity, you can also divide the materials based on their manufacturing settings:
- Direct Materials: These are primary and are of use in creating finished products. For instance, wood is the primary material in the production of furniture, chairs, beds and tables. You can manufacture shoes, bags and purses with leather.
- Indirect Materials: These materials aid in the production process but are not part of the final product. Examples include glue, nails, and varnish used to make wooden furniture. Also, buckles, metal hoops and lining fabric are used to make leather goods.
All these materials that make the products move through certain processes before they reach the hand of the consumer. What are those steps? Let’s see the long road that they take.
Journey of Raw Materials
The road that these materials take is a fascinating logistical feat. The supply chain orchestrated the material processing from source to production. It finds suppliers ensuring on-time deliveries. It does all of this keeping costs down and minimising disruptions.
Let’s see the detailed process:
1.Extraction:
This is where the journey starts. The extraction site could be anywhere- a cotton field or a mine ore. Workers extract the materials from the source in its raw form and send them over to processing. This is where the journey starts. The extraction site could be anywhere- a cotton field or a mine ore. Workers extract the materials from the source in its raw form and send them over to processing.
2.Processing:
Not all materials are ready for prediction. For instance, if you extract cotton, you would have to remove the seeds. If you extract iron ore, you would have to crush it and refine it to make it usable. Also, woods need sawing before you can shape them into furniture.
3.Transportation:
Once the materials have undergone processing, the materials head to the next destination. Then load them onto trucks or cargo ships so they can go to the factories.
4.Transformation:
The material here is turned into actual products. So, leather pieces become belts and bags. Manufacturers weave cotton threads into fabric and so forth.
5.Distribution:
The finished products like T-shirts, steel appliances, or chairs then go to the warehouse distribution centres. These hubs are the central point for transportation to stores.
6.Retail:
Products reach their final destination. The retail stores display the products on shelves and they are ready to be purchased. For instance, when you buy new fashion clothes fresh off the rack or electronics from the shops.
Each step involves logistics quality control to ensure timely delivery and proper maintenance. All of these are crucial to have an efficient supply chain.
So, how do the materials move through the supply chain? Let’s see with raw materials examples.
Raw Material Journey to Become a Sofa in the E-commerce Industry
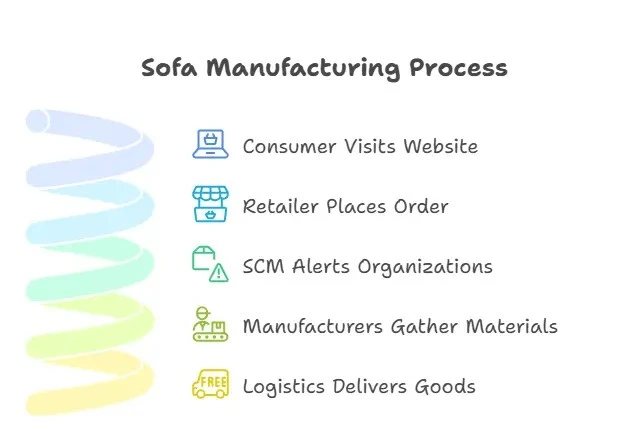
Let’s say we see the journey of the sofa couch in your house. How did the making materials become the couch and where did they come from and what is the manufacturing process?
Phase 1: Consumer Visits an ECommerce Website and Orders a Sofa
A customer likes a sofa they see online. They place an order for it. Even though they see that the sofa is out of stock they set an alert to make the purchase when it’s available. Once it is, they make the purchase. Or some customers are willing to enter the waitlist for the sofa.
Phase 2: Retailer Places an Order for Sofas
The sofa is out of stock but recently it was in an ad with a popular actor. According to predictive analytics, there is a huge demand for it now. So the retailer places an order for 500 sofas, which he assesses would sell over the next three months. He places the requests in the internal order system of the supply chain management (SCM).
Phase 3: SCM Places the Order and Alerts Key Supply Chain Organizations of the Requirements
SCM manages the order and their software notifies suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and logistics in the global supply chain. This product is sourced and manufactured through arrangements that the retailer has with suppliers and furniture builders. The businesses receive a demand notification for 500 sofas and begin the sourcing and manufacturing process.
Phase 4: Manufacturers Gather Raw Materials with the Help of Suppliers
The manufacturers are aware of how much material they need to build a sofa. They calculate the quantity of raw materials they need and then ask for their supply from the upstream suppliers. Here are some of the items they would need:
- Wood to build a sofa frame
- Fabric in various colours covers the sofa
- Foam from the sofa cushions
- Fastening will help them put the frames together and attach the fabric and foam
- Other parts.
Those upstream suppliers may ask for more raw materials. For instance, a fabric manufacturer needs to source cotton and dye to make the fabric.
Let’s see the next steps in this journey.
Phase 5: Logistics Delivers Raw Goods and the Manufacturer Receives Them
Once you receive the materials, the factory starts to manufacture as per the customer’s specifications, ensuring costs and quality standards are met. Once the sofas are complete, personnel load them into shipping containers.
Logistics plays a crucial role in ensuring that the raw materials reach the manufacturing facility promptly and efficiently. These providers coordinate the transportation of materials via road, rail and air freight, ensuring timely delivery.
When the items arrive, manufacturers inspect them to verify if they meet quality standards and order specifications. This process includes checking for any damage during transit and confirming quantities. Once verified, these materials move into inventory and confirm quantities.
Conclusion
You now know that every product starts from the “raw materials” stage. They usually have to go through a complex path to finally become products that are ready for consumers to use. Throughout this lengthy process, these materials are at the mercy of the supply chain players. These supply chain players need good planning, tactics and logistics experts like the ones from Qodenext and be ready to face bottlenecks to ensure a smooth and efficient supply chain. This way all the key players can ensure a smooth-running system.
FAQs: From Seed to Shelf: Understanding the Journey of Raw Materials in Everyday Products
1.How does the source of materials impact the supply chain?
Source has a direct impact on the supply chains. The distance between the source and the processing facilities can increase transportation costs; factors like geopolitics and sustainability also affect the availability of these materials. Most manufacturers now practice ethical sourcing as per customer demands.
2.What are some challenges in tracking materials in supply chains?
Tracking materials from source to shelf can become difficult due to the complex nature of supply chains. It has various players, and sourcing materials is hard as each is from different countries with unique regulations and laws. Some suppliers may not be transparent about their sourcing practices. Inconsistent or incomplete data can make it hard to track the movement of materials.
3.Why do you need a transparent supply chain?
It mitigates risks associated with disruptions and unethical sourcing. Consumers are increasingly interested in ethical companies. Lastly, it provides better visibility and leads to better planning and cost savings.
4.Why is quality control important at each stage of the raw material journey?
Quality checks during extraction, processing, and upon receipt at manufacturing ensure materials meet standards, preventing defects in the final product and reducing costly rework or rejects.
5.How do logistics impact the timely delivery of raw materials for production?
Efficient transportation networks and logistics providers are vital to move raw materials quickly and safely from extraction sites to processing plants and manufacturers, reducing delays that could halt production.
6.What role do suppliers play within the raw material supply chain?
Suppliers source raw materials, often coordinating further upstream with farmers, miners, or other producers, and ensure materials are available on time, conforming to quality, price, and sustainability standards.
7.How does ethical sourcing influence raw material supply chains?
Ethical sourcing ensures materials are obtained responsibly, respecting labor rights and environmental standards, which enhances brand reputation and meets growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
8.What challenges do manufacturers face when handling indirect raw materials?
Indirect materials, though not part of the finished product, must be managed carefully to avoid production delays. Challenges include maintaining adequate stock levels and ensuring timely availability for assembly or finishing processes.
9.How can technology improve tracking of raw materials in global supply chains?
Technologies like RFID, blockchain, and IoT enable real-time tracking of raw materials, enhance transparency, improve inventory accuracy, and help identify bottlenecks or risks early.
10.What happens if raw materials are delayed or damaged during transportation?
Delays or damage can disrupt production schedules, increase costs, and affect product delivery timelines. Robust logistics planning, quality checks on arrival, and contingency measures help mitigate these risks.






