Introduction:
In the intricate web of supply chain management, Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) play a pivotal role. These alphanumeric codes serve as unique identifiers for products, facilitating efficient inventory management. Understanding the nuances of SKUs is crucial for businesses, especially in the realms of e-commerce and logistics. This article delves into the intricacies of SKUs, exploring their meaning, role in inventory, and best practices for SKU management.
Stock Keeping Unit
In the realm of retail and inventory management, SKU, or Stock Keeping Unit, plays a pivotal role in streamlining operations and ensuring efficient tracking of products. SKU is a unique alphanumeric code assigned to each distinct product in a retailer’s inventory, acting as a fingerprint that distinguishes it from other items.
SKU is a shorthand code that encapsulates crucial information about a product, such as its size, color, style, and manufacturer. This distinct identifier allows businesses to manage their inventory with precision, minimizing errors and enhancing overall efficiency.
SKU, often considered the DNA of inventory, is a unique code that distinguishes each product in a company’s catalog. Its significance lies in its ability to facilitate accurate tracking, monitoring, and management of inventory items.
SKU is a unique alphanumeric code assigned to each distinct product in a retailer’s inventory. This identifier serves as a key reference point for tracking and managing products throughout the entire ecommerce supply chain. Essentially, the SKU acts as a digital fingerprint for products, enabling seamless organization and efficient inventory management.
SKU Structure:
Typically, an SKU comprises a combination of letters and numbers, creating a standardized format for easy interpretation. For example, an SKU for a specific shoe model might include the brand initials, size, and color code, providing a quick reference for both staff and automated systems.
Importance of SKU in Inventory Management:
- Accuracy and Precision: SKUs help in maintaining accurate records of inventory levels, reducing the risk of errors in tracking and restocking.
- Efficient Order Fulfillment: When integrated into order processing systems, SKUs expedite the picking and packing process, ensuring that the correct products are shipped to customers promptly.
- Data Analysis: SKUs facilitate in-depth data analysis, allowing businesses to identify top-performing products, forecast demand, and optimize stocking levels.
Role in E-Commerce:
In the digital age, SKUs are indispensable for online retailers. They not only enable seamless order processing but also contribute to a positive customer experience by preventing shipping errors and delays.
Creating Effective SKUs:
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent format for SKUs across all products to avoid confusion and enhance system reliability.
- Uniqueness: Ensure each SKU is unique to prevent overlap or misidentification of products.
Integration with Technology:
- Barcode Scanning: Incorporate SKUs into barcode systems for quick and accurate product identification.
- Point of Sale (POS) Systems: Integrate SKUs with POS systems to streamline transactions and update inventory in real-time.
Future Trends and Innovations:
- As technology advances, the role of SKUs continues to evolve. Automation, machine learning, and artificial intelligence are increasingly being employed to enhance SKU management and optimize inventory processes.
SKUs are the backbone of effective inventory management, providing a standardized and efficient way to identify, track, and analyze products. Implementing a robust SKU system is essential for businesses looking to stay competitive in the dynamic landscape of retail and e-commerce.
SKU Supply Chain
In the intricate landscape of supply chain management, the SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) plays a pivotal role in streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency. SKU, in essence, is a unique identifier assigned to each distinct product in a company’s inventory. In the context of supply chain management, the effective utilization of SKUs can significantly impact various aspects of the process, from warehousing to distribution. Let’s delve into the key considerations for optimizing SKU management within the supply chain.
Significance of SKU:
1. SKU Standardization:
Standardizing SKUs across the supply chain is essential for seamless communication and coordination between different stages of the process. This standardization ensures clarity and consistency, reducing the likelihood of errors and mismanagement.
2. Warehousing Efficiency:
SKUs contribute significantly to efficient warehousing. Proper SKU classification and organization enable swift retrieval and fulfillment of orders. This efficiency is crucial in meeting customer demands and minimizing lead times.
3. Inventory Accuracy:
The accuracy of inventory management relies heavily on the precision of SKUs. Assigning unique SKUs to products helps in avoiding confusion, preventing stockouts, and facilitating precise reorder points based on historical data and demand forecasting.
4. Demand Forecasting and SKU Rationalization:
SKU data is instrumental in demand forecasting. Analyzing SKU performance allows for strategic SKU rationalization, wherein underperforming or obsolete items can be identified and removed, optimizing inventory and warehouse space.
5. Distribution and Logistics:
In the distribution phase, SKUs play a crucial role in load planning, order picking, and route optimization. Efficient SKU management ensures that the right products reach the right destinations at the right time, minimizing delays and costs.
6. Technology Integration:
Embracing advanced technologies, such as RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) and barcode systems, enhances SKU visibility and traceability. Integrating these technologies into the supply chain streamlines operations and reduces the likelihood of errors.
7. Supplier Collaboration:
Collaborating with suppliers on SKU-related information fosters transparency and improves communication. This collaboration extends to ensuring that suppliers adhere to SKU standards, facilitating smoother integration into the supply chain.
SKU management is a linchpin in the optimization of supply chain operations. From the warehouse to the end consumer, the effective use of SKUs enhances accuracy, efficiency, and overall performance. Embracing standardized practices, leveraging technology, and fostering collaboration throughout the supply chain are paramount for unlocking the full potential of SKU management. As businesses navigate the dynamic landscape of supply chain intricacies, a strategic approach to SKU optimization becomes not just a necessity but a competitive advantage.
What Is SKU In Ecommerce
In the dynamic world of ecommerce, mastering the intricacies of product management is crucial for success. One fundamental aspect that plays a pivotal role in this realm is the Stock Keeping Unit, commonly known as SKU. In this guide, we will delve into the nuances of SKU in ecommerce, shedding light on its definition, significance, and best practices.
Significance of SKU in Ecommerce:
1. Inventory Management:
SKUs facilitate precise tracking of products, helping ecommerce businesses maintain accurate inventory levels. This is crucial for preventing overstock or stockouts, ensuring a streamlined supply chain.
2. Order Fulfillment:
Efficient order processing relies on the unique identification provided by SKUs. With accurate SKU information, ecommerce platforms can swiftly locate, pick, and dispatch products, enhancing overall order fulfillment speed.
3. Data Analysis:
SKUs play a pivotal role in data analysis, providing insights into product performance, sales trends, and customer preferences. Ecommerce businesses can leverage SKU data to make informed decisions and optimize their product offerings.
4. Customer Experience:
The use of SKUs contributes to a better customer experience by minimizing errors in order processing. Customers receive the correct products promptly, fostering trust and satisfaction.
5. Marketing and Merchandising:
Ecommerce businesses can strategically use SKUs for targeted marketing campaigns and personalized merchandising. By understanding the performance of specific SKUs, businesses can tailor their promotional efforts for maximum impact.
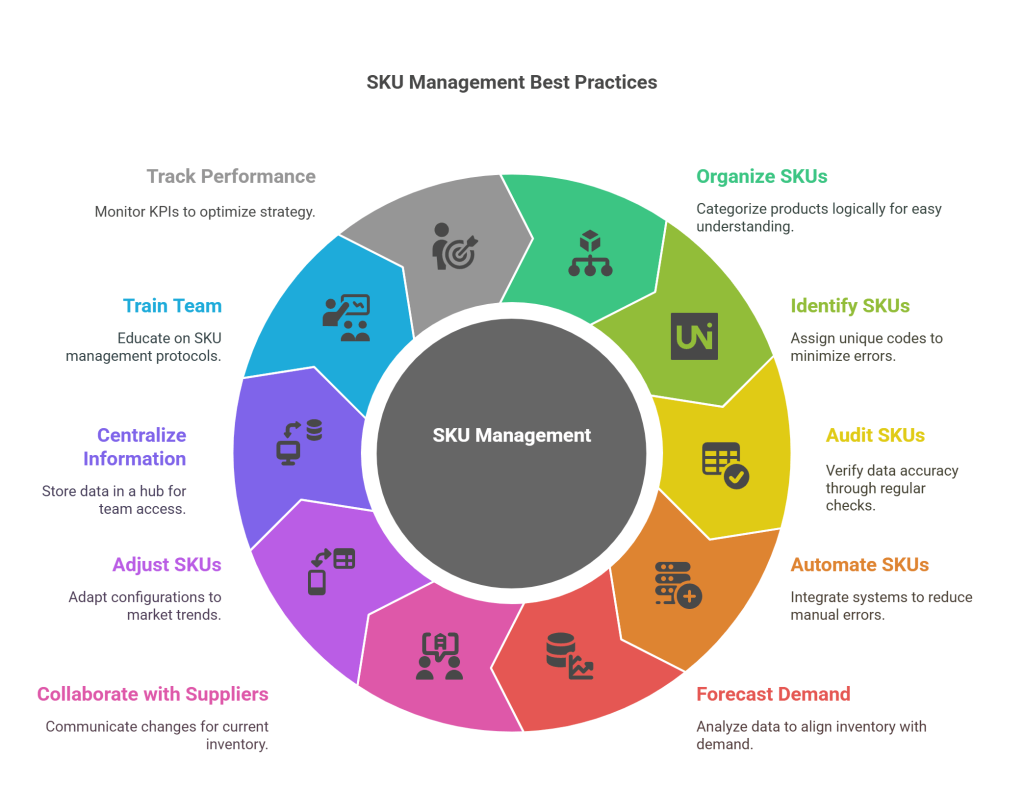
Best Practices for Managing SKUs:
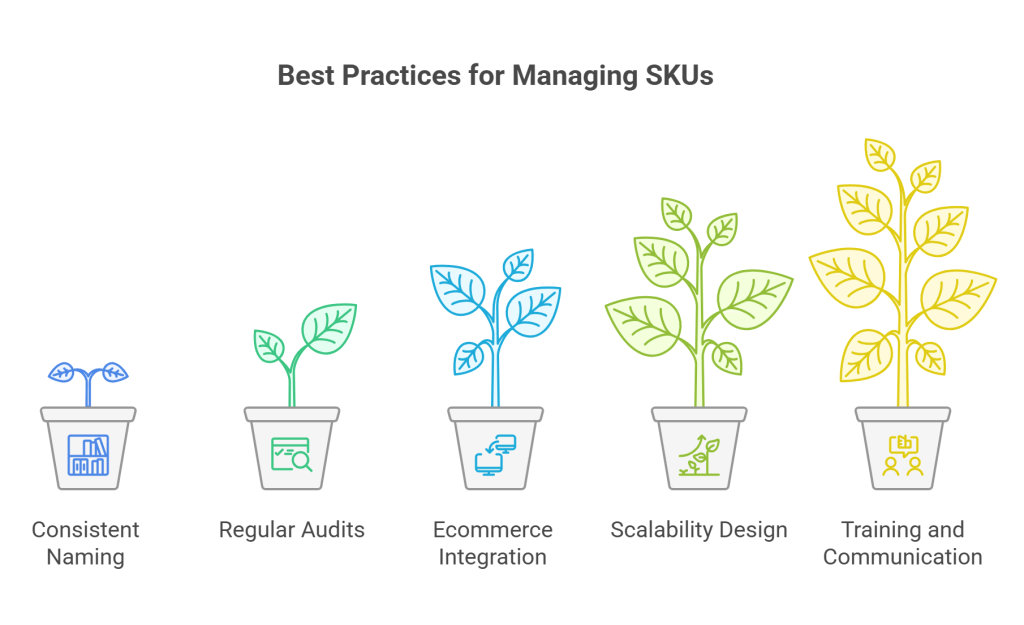
1. Consistent Naming Conventions:
Establish a standardized system for naming and formatting SKUs to avoid confusion. Consistency in SKU creation streamlines inventory management processes.
2. Regular Audits and Updates:
Conduct regular audits of your SKU database to identify and rectify discrepancies. Ensure that SKUs are updated to reflect changes in product attributes or variants.
3. Integration with Ecommerce Platforms:
Integrate your SKU system with your ecommerce platform for seamless information flow. This integration enhances overall efficiency in managing products, orders, and inventory.
4. Scalability:
Design your SKU system with scalability in mind. As your ecommerce business grows, having a scalable SKU structure ensures that you can efficiently manage an expanding product catalog.
5. Training and Communication:
Ensure that your team understands the importance of SKUs and follows best practices in SKU management. Clear communication regarding SKU conventions and updates is crucial for maintaining accuracy.
Understanding the role of SKU in ecommerce is paramount for successful inventory management and overall business efficiency. By implementing best practices and recognizing the significance of SKUs, ecommerce businesses can navigate the complexities of product management with precision and agility.
What Is SKU In Inventory
SKU, or Stock Keeping Unit, is a critical component of effective inventory management. In this article, we will delve into the significance of SKU, exploring its definition, role in inventory systems, and the benefits it brings to businesses.
Importance in Inventory Systems:
SKU plays a pivotal role in inventory systems by facilitating precise tracking and management of individual products. It acts as a bridge between physical products and digital records, streamlining the monitoring of stock levels, reordering processes, and overall inventory control.
Role in Efficient Inventory Management:
Efficient inventory management relies heavily on the utilization of Stock Keeping Units. Assigning a unique identifier to each product allows businesses to accurately monitor stock movement, identify popular items, and optimize reordering strategies. This, in turn, minimizes the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
Benefits of Using SKUs:
1. Accuracy in Tracking:
SKUs enhance accuracy in tracking inventory. By using a unique code for each product, businesses can precisely monitor the quantity and movement of items, reducing errors in record-keeping.
2. Improved Order Fulfillment:
The use of SKUs streamlines the order fulfillment process. With a well-organized SKU system, businesses can quickly locate products, pick them accurately, and fulfill customer orders promptly.
3. Enhanced Forecasting:
Stock Keeping Units contribute to better demand forecasting. By analyzing SKU-level data, businesses can identify trends, understand customer preferences, and make informed decisions about inventory levels and product assortment.
4. Facilitates Reporting and Analysis:
SKUs simplify reporting and analysis. Businesses can generate detailed reports on individual product performance, sales trends, and inventory turnover, aiding strategic decision-making.
Implementing an Effective SKU System:
1. Clear Naming Conventions:
Establish clear and consistent naming conventions for SKUs to avoid confusion and ensure uniformity across the inventory.
2. Integration with Technology:
Integrate SKU systems with advanced inventory management software to leverage automation, reduce manual errors, and enhance overall efficiency.
3. Regular Audits and Updates:
Conduct regular audits of Stock Keeping Unit data to identify and rectify discrepancies. Update SKUs as needed to accommodate changes in product attributes or variations.
Understanding the role of SKU in inventory management is paramount for businesses seeking operational efficiency and accuracy in their supply chain processes. By implementing and maintaining an effective SKU system, companies can streamline their operations, improve customer satisfaction, and make data-driven decisions to stay competitive in the market.
SKU Meaning In Logistics
In logistics, the term SKU, which stands for Stock Keeping Unit, plays a pivotal role in managing inventory efficiently. SKU refers to a unique code or identifier assigned to a specific product or item within a company’s inventory. This alphanumeric code helps streamline the tracking and management of products, contributing significantly to the overall logistics and supply chain processes.
Key Points about SKU in Logistics:
1. Unique Identification:
An SKU serves as a unique fingerprint for each product in a company’s inventory. It distinguishes items from one another, preventing confusion and facilitating precise tracking.
2. Streamlining Operations:
The repetitive use of the SKU meaning in logistics underscores the importance of this term in streamlining logistical operations. By assigning a distinct SKU to each product, businesses can easily monitor stock levels, trace product movements, and optimize warehouse organization.
3. Efficient Inventory Management:
Stock Keeping Unit implementation is crucial for effective inventory management. With a designated code for each product, businesses can quickly access information about stock levels, reorder points, and product specifications, aiding in the prevention of overstock or stockouts.
4. Order Fulfillment Accuracy:
In the context of logistics, SKU plays a vital role in maintaining order fulfillment accuracy. Warehouse staff can rely on Stock Keeping Units to pick and pack products accurately, reducing errors in shipment and improving customer satisfaction.
5. Data Analysis and Reporting:
The repetitive inclusion of the keyword emphasizes the significance of SKU in data analysis and reporting. By analyzing SKU-specific data, businesses can gain insights into product performance, demand patterns, and overall inventory health.
6. Supply Chain Visibility:
SKUs enhance supply chain visibility by providing a standardized way to identify and trace products throughout the entire logistics process. This visibility is crucial for making informed decisions and responding promptly to changes in demand or supply.
7. Barcode Integration:
Stock Keeping Units are often associated with barcodes, enabling automated scanning and data capture. Barcode integration simplifies the recording of product movements, reducing manual errors and enhancing the overall efficiency of logistics operations.
SKU, or Stock Keeping Unit, is a fundamental concept in logistics that significantly contributes to efficient inventory management, order fulfillment accuracy, and overall supply chain optimization. The repeated emphasis on the keyword “SKU meaning in logistics” highlights its critical role in the logistics landscape, underscoring the importance of this unique identifier in the world of inventory and supply chain management.
SKU Management Best Practices
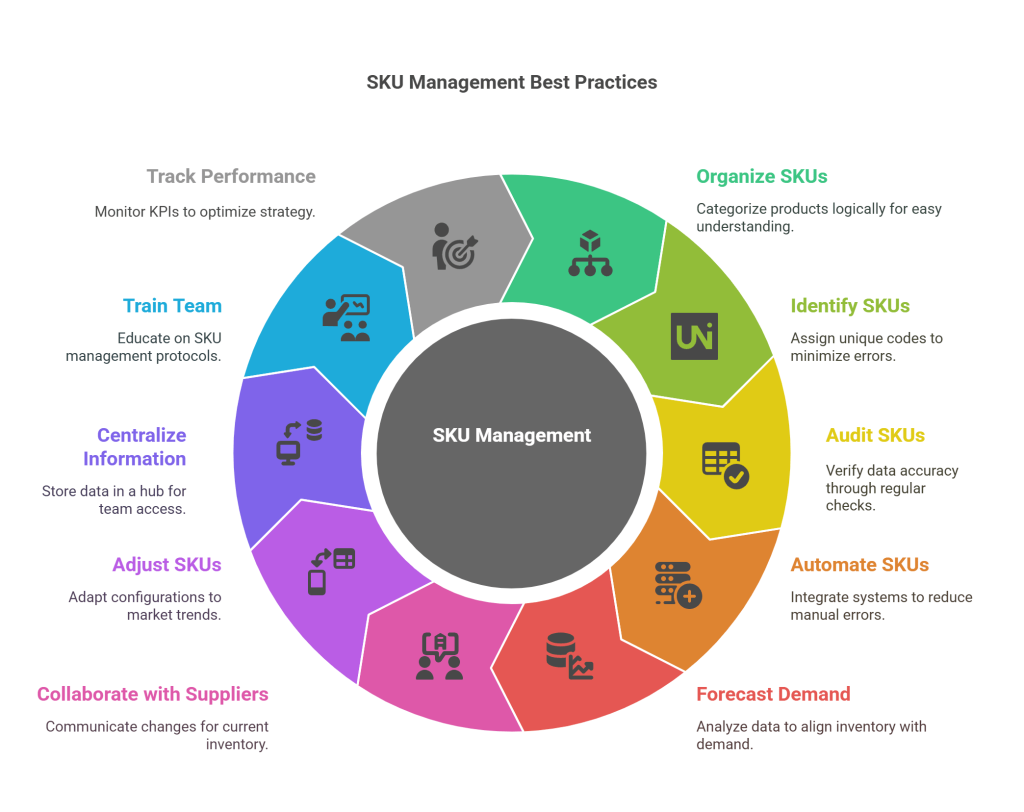
Effective SKU management is crucial for streamlined inventory operations and overall business success. SKU, or Stock Keeping Unit, management involves organizing and tracking individual product variants to optimize inventory control and enhance customer satisfaction. Implementing best practices in SKU management ensures efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability to market dynamics.
1. SKU Organization:
Efficient Stock Keeping Unit management starts with a well-organized system. Categorize products logically based on characteristics such as size, color, and model. Utilize a consistent naming convention to make SKUs easily understandable for your team.
2. Clear Identification:
Assign unique and easily distinguishable codes to each SKU. Clear identification minimizes errors in order fulfillment and facilitates quick retrieval during stock counts.
3. Regular Audits and Reviews:
Conduct regular audits to verify the accuracy of Stock Keeping Unit data. Periodic reviews help identify obsolete or slow-moving items, allowing for strategic adjustments to prevent overstocking or stockouts.
4. Automation Integration:
Integrate SKU management with automated systems to reduce manual errors and enhance efficiency. Utilize technology for tasks such as order processing, tracking inventory levels, and generating real-time reports.
5. Forecasting and Demand Planning:
Implement robust forecasting and demand planning practices to anticipate SKU demand accurately. Analyzing historical data and market trends aids in aligning inventory levels with customer expectations.
6. Supplier Collaboration:
Foster strong relationships with suppliers and communicate effectively regarding Stock Keeping Unit changes, introductions, or discontinuations. Timely information exchange ensures that your inventory reflects the most current product offerings.
7. Flexibility in SKU Adjustments:
Maintain flexibility to adapt Stock Keeping Unit configurations based on market trends and customer preferences. Quickly adjust to changes in demand by adding or modifying SKUs as needed.
8. Centralized Information Hub:
Establish a centralized information hub where all Stock Keeping Unit-related data is stored. This ensures that your team has access to accurate and up-to-date information, fostering better decision-making.
9. Training and Communication:
Provide comprehensive training to your team on Stock Keeping Unit management protocols. Effective communication ensures that everyone understands the importance of accurate SKU data and follows established procedures.
10. Performance Metrics Tracking:
Develop key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the effectiveness of SKU management. Monitor metrics such as turnover rates, order accuracy, and stockout frequency to continuously optimize your SKU strategy.
Implementing these Stock Keeping Unit management best practices will not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to maintaining a competitive edge in the market. Regularly review and adapt your SKU management strategy to meet evolving business needs and market trends. Stock Keeping Unit management best practices should be seen as a dynamic process that evolves alongside your business growth and industry changes.
SKU In Supply Chain Management
In the realm of Supply Chain Management (SCM), SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) stands out as a pivotal element ensuring efficiency and streamlined operations. SKU is essentially a unique code assigned to each distinct product within a company’s inventory, and its significance cannot be overstated in the logistics landscape.
1. Distinct Identification:
SKU provides a distinct identification to each product in a company’s inventory, facilitating accurate tracking and management of stock. This distinctiveness ensures that each item is easily recognizable, minimizing errors in order fulfillment and inventory management.
2. Efficient Inventory Control:
The repetition of the SKU keyword is indicative of its paramount role in maintaining efficient inventory control. Implementing SKUs allows for precise monitoring of stock levels, enabling businesses to replenish products in a timely manner and prevent stockouts, which can be detrimental to customer satisfaction.
3. Streamlined Order Fulfillment:
In the context of order fulfillment, SKU acts as a linchpin. Repeating the keyword emphasizes its role in streamlining the process by enabling quick and error-free identification of products, leading to faster and more accurate order processing.
4. Enhanced Demand Forecasting:
The strategic repetition of SKU underscores its importance in demand forecasting. By analyzing SKU-level data, businesses can gain insights into the popularity of specific products, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding production, marketing, and inventory stocking.
5. Improved Traceability and Visibility:
SKU repetition emphasizes the role of SKU in enhancing traceability and visibility throughout the supply chain. From the manufacturer to the end consumer, each step can be tracked efficiently, fostering transparency and accountability at every stage of the product’s journey.
6. Customization and Personalization:
SKUs pave the way for customization and personalization of product offerings. The repetition of the keyword highlights how SKU facilitates the management of diverse product variants and configurations, catering to the evolving preferences of consumers.
7. Optimized Supply Chain Performance:
Ultimately, the recurrence of SKU emphasizes its overarching impact on optimizing overall supply chain performance. Efficient inventory management, accurate order fulfillment, and data-driven decision-making contribute to a responsive and agile supply chain that can adapt to market dynamics.
The strategic use of the SKU keyword throughout this content underscores its critical role in Supply Chain Management. Its implementation is not merely a technicality but a strategic approach that can significantly impact the efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability of a company’s supply chain operations.
Conclusion:
SKUs (Stock Keeping Units) are the backbone of efficient inventory and supply chain management. By providing unique identifiers for each product, SKUs enable accurate tracking, streamlined order fulfillment, and insightful data analysis.
Whether in retail, e-commerce, or logistics, implementing a consistent and scalable SKU system enhances operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. As technology evolves, integrating SKUs with automation and advanced analytics will further optimize inventory processes and give businesses a competitive edge. Qodenext emphasizes the significance of a well-organized SKU system. Implementing these insights ensures a smoother journey through the intricate corridors of supply chain management.
FAQs: SKU (Stock Keeping Unit): What Is It And How Is It Used?
1. What does SKU stand for?
SKU stands for Stock Keeping Unit, a unique alphanumeric code assigned to each distinct product in inventory.
2. Why are SKUs important for businesses?
SKUs help maintain accurate inventory records, speed up order fulfillment, and enable detailed data analysis for better decision-making.
3. How is an SKU structured?
An SKU typically combines letters and numbers that represent product attributes like brand, size, and color.
4. How do SKUs improve order fulfillment?
By uniquely identifying products, SKUs reduce errors during picking and packing, ensuring customers receive the correct items promptly.
5. Can SKUs be used in e-commerce?
Yes, SKUs are essential in e-commerce for managing large inventories, streamlining order processing, and enhancing customer experience.
6. What are best practices for SKU management?
Best practices include maintaining consistent naming conventions, ensuring SKU uniqueness, performing regular audits, and integrating SKUs with inventory systems.
7. How do SKUs aid demand forecasting?
SKU-level sales data allows businesses to identify trends and adjust inventory levels to meet customer demand effectively.
8. What role do SKUs play in warehouse management?
SKUs enable efficient organization and retrieval of products, reducing lead times and improving warehouse productivity.
9. How does technology integrate with SKUs?
Technologies like barcode scanning, RFID, and POS systems use SKUs for quick identification and real-time inventory updates.
10. Can SKUs help in supplier collaboration?
Yes, sharing standardized SKU information with suppliers improves transparency, accuracy, and coordination in the supply chain.







