
As a business manager or owner, you must have come across problems. These challenges and roadblocks are common to rise. From technological advancements to shifting market trends, staying ahead requires a comprehensive understanding of common industry problems and solutions to overcome them.
For successful and sustainable growth and success, you must address these roadblocks which hinder your progress. But what are some of the most common industry problems? Here’s a comprehensive guide on the top 7 Common Industry Problems and Solutions, how to solve them. Read on!
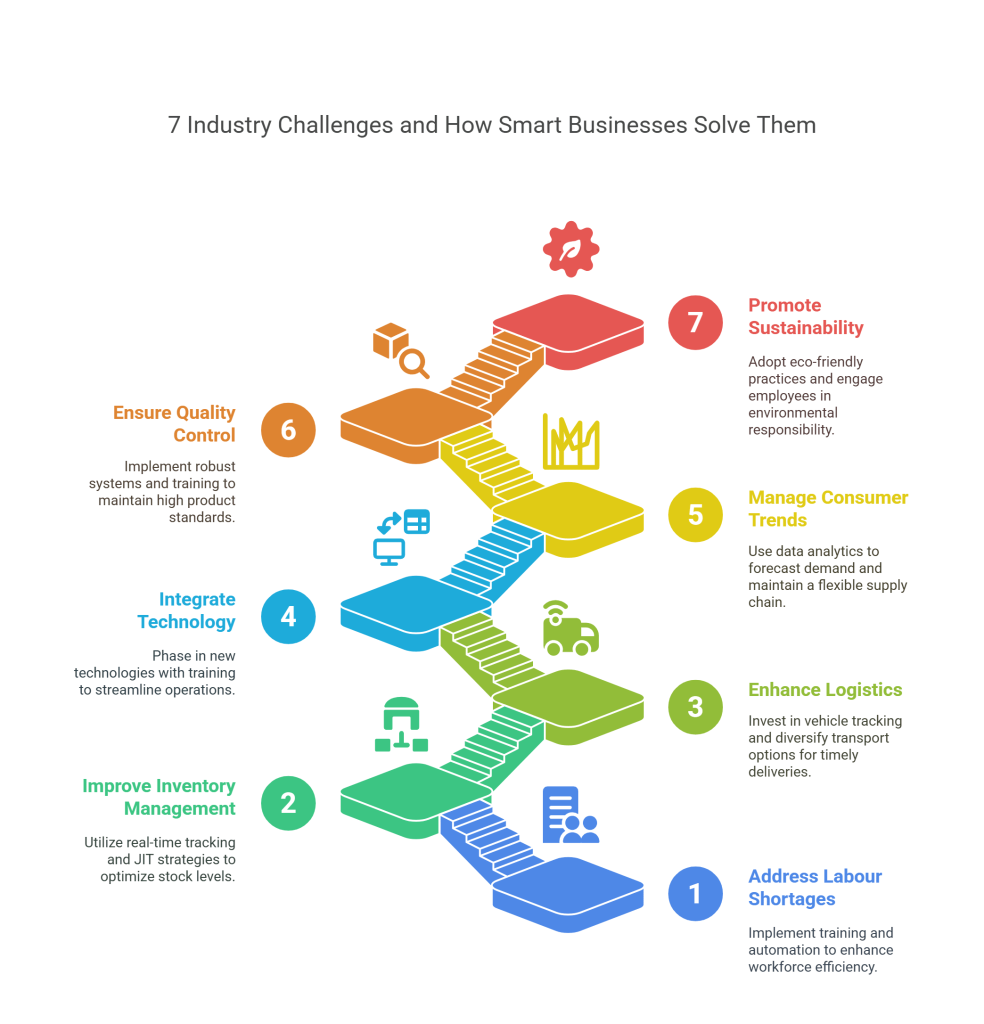
1. Labour Shortage and Workforce Inefficiency
The Problem:
Many industries today face a persistent challenge in attracting and retaining skilled labor. The shortage of qualified professionals creates bottlenecks in production lines, delays in service delivery, and forces companies to operate below optimal capacity.
For instance, even before the COVID-19 pandemic, data indicated millions of job vacancies remained unfilled due to a mismatch between skills demanded and those available in the labor market. The pandemic only worsened this gap as many workers left industries or sought different roles, making it harder for companies to find the right talent.
Additionally, workforce inefficiency often compounds the problem. Companies may have enough employees on paper, but poor deployment and lack of clear role allocation result in underutilization or employee burnout. When workers are either overwhelmed with tasks or left idle without meaningful work, job satisfaction decreases, and turnover rates rise, costing businesses time and money.
The Solution:
Addressing labor shortage and inefficiency requires a multifaceted approach. First, investing in comprehensive training programs is essential. Companies should focus on upskilling their existing workforce so employees can adapt to changing technologies and take on diverse roles. For example, cross-training warehouse workers to operate machinery or manage logistics can increase workforce flexibility.
Flexible hiring models also expand the talent pool. Offering part-time roles, remote work options, or project-based contracts attracts a wider range of candidates who may not be available for full-time traditional positions. These models help meet fluctuating labor demands without long-term commitment.
Technology plays a vital role. Automating repetitive manual tasks with robotics, AI-powered tools, or software solutions can reduce dependency on human labor for mundane activities, allowing workers to focus on strategic, high-impact tasks. Moreover, creating a positive work culture with clear growth pathways, recognition, and competitive benefits can improve retention and motivation.
Example:
A global logistics company experienced a driver shortage post-pandemic that delayed deliveries. They launched an internal training program that enabled warehouse staff to become certified delivery drivers using GPS navigation systems. This initiative not only filled immediate labor gaps but boosted employee engagement by offering new skills and career advancement opportunities.
2. Inventory Management Challenges
The Problem:
Inventory management stands at the core of every successful business, yet many companies struggle to maintain optimal stock levels. Poor inventory control results in overstocking, which ties up capital and increases storage costs, or understocking, which leads to missed sales and unhappy customers. Lack of transparency in the supply chain further complicates this issue, making it difficult to track inventory accurately or anticipate demand fluctuations.
Traditional inventory systems often fall short of providing real-time insights, leading to errors, wastage, and delays in replenishment.
The Solution:
Adopting modern inventory tracking technologies is a game-changer. Solutions like Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), barcode scanning, and Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled sensors allow businesses to monitor inventory levels in real-time. These technologies offer instant visibility into stock availability, movement, and shelf life, enabling proactive decision-making.
Moreover, inventory management strategies such as Just-In-Time (JIT) delivery help maintain lean stock levels by ordering goods only when needed, reducing storage costs and minimizing waste. ABC analysis categorizes inventory based on sales value, allowing managers to prioritize high-value items for tighter control.
Integrating inventory management software with sales and procurement systems ensures smooth coordination across departments, reducing errors and improving replenishment cycles.
Example:
A mid-sized electronics retailer implemented RFID tags across its warehouse and store locations. This technology provided accurate stock data in real-time, reduced manual stock counts by 80%, and enabled faster response to demand spikes during festive seasons, boosting sales and customer satisfaction.
3. Delay in Logistics and Transportation
The Problem:
Logistics delays disrupt the smooth flow of goods and information throughout the supply chain, leading to late deliveries, increased operational costs, and damaged customer trust.
Delays can be caused by traffic congestion, vehicle breakdowns, inefficient route planning, customs clearance issues, or communication gaps between supply chain partners.
In today’s fast-paced market, even minor logistics delays can cause significant ripple effects, affecting inventory availability, production schedules, and ultimately the customer experience.
The Solution:
Businesses must embrace advanced technological solutions such as GPS-enabled real-time tracking systems to monitor the location and status of shipments continuously. These tools provide visibility, allowing proactive response to delays or route disruptions.
Diversifying transportation channels — using a mix of trucks, rail, air, or sea freight — increases flexibility and reduces dependence on a single mode vulnerable to delays. Strengthening collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers through integrated communication platforms ensures smoother coordination.
Regular maintenance of vehicles, investment in reliable transportation infrastructure, and employing data analytics to optimize routes further minimize delays and improve delivery timelines.
Example:
An e-commerce company integrated a GPS tracking system for its fleet and partnered with multiple courier services, allowing dynamic rerouting during traffic or weather disruptions. This strategy improved delivery punctuality by 25% and enhanced customer satisfaction during peak sales periods.
4. Technological Integration in Industry
The Problem:
In many industries, technological integration remains a significant challenge. Companies hesitate to adopt new digital tools due to perceived complexity, cost concerns, or resistance to change among employees. However, failure to innovate leads to stagnation, inefficiencies, and loss of competitive advantage.
Without seamless technology adoption, businesses struggle with data silos, manual processes, and communication breakdowns that reduce overall productivity and increase errors.
The Solution:
Successful technology integration requires a strategic approach. Start with identifying the most impactful technologies aligned with business goals—such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) software, or automation tools.
Pilot testing new technologies on a smaller scale helps identify issues and fine-tune implementation before company-wide rollout. Employee training is crucial to build confidence and skill in using new systems, reducing resistance and ensuring smooth adoption.
Leadership must actively promote digital transformation by clearly communicating benefits and involving teams throughout the process.
Example:
A manufacturing firm introduced an ERP system to unify procurement, inventory, and production data. Before full deployment, they conducted a pilot in one factory unit and provided hands-on training. The successful pilot paved the way for seamless implementation across all locations, improving operational visibility and decision-making.
5. Consumerism Trends and Seasonal Demand Fluctuations
The Problem:
Industries, especially retail and manufacturing, frequently grapple with unpredictable consumer behavior and seasonal demand spikes. Sudden surges in product demand can cause stockouts, delivery delays, and missed revenue opportunities. Conversely, off-season periods may lead to excess inventory and cash flow issues.
Failure to anticipate these trends results in inefficient resource allocation and lost market share.
The Solution:
Creating a flexible, agile supply chain is critical. Businesses must monitor sales data continuously, using predictive analytics to identify upcoming demand trends and seasonal patterns. This allows timely adjustments in production and inventory levels.
Maintaining buffer stock or safety inventory ensures preparedness for unexpected demand surges. Collaborative planning with suppliers and distributors facilitates quick response and replenishment.
Effective communication with customers about product availability and delivery times helps manage expectations during peak periods.
Example:
A fashion retailer used historical sales data and social media trend analysis to forecast demand for seasonal clothing lines. They adjusted procurement schedules accordingly and collaborated closely with suppliers to speed up deliveries, reducing stockouts by 40% during holiday seasons.
6. Quality Control Issues
The Problem:
Poor quality control leads to product defects, customer complaints, and increased return rates, damaging brand reputation and profitability. Inconsistent quality can stem from inadequate inspection processes, lack of employee training, or supplier variability.
Ignoring quality issues results in long-term customer distrust and lost business opportunities.
The Solution:
Implementing robust quality control systems is essential. This includes multiple inspection points during production, strict adherence to standards, and continuous monitoring using statistical process control techniques.
Regular employee training on quality standards and best practices helps prevent errors. Encouraging a culture of quality, where workers feel responsible and empowered to flag issues early, improves overall outcomes.
Additionally, collecting and analyzing customer feedback provides valuable insights to identify recurring problems and implement corrective actions promptly.
Example:
An electronics manufacturer introduced automated testing machines on the assembly line, coupled with quarterly training sessions for staff. This proactive approach reduced defects by 30% and enhanced customer satisfaction scores significantly.
7. Sustainability and Environmental Impact
The Problem:
Increasing environmental regulations and growing consumer awareness force industries to adopt sustainable practices. Ignoring sustainability harms the environment and risks regulatory penalties, loss of customer trust, and missed opportunities in green markets.
Many companies struggle to balance sustainability goals with operational efficiency and cost constraints.
The Solution:
Building a sustainable supply chain begins with energy-efficient technologies and waste reduction programs. Investing in renewable energy sources, recycling initiatives, and eco-friendly materials lowers environmental impact.
Product innovation focused on sustainability—such as biodegradable packaging or energy-saving designs—meets consumer demand while supporting corporate responsibility.
Training employees on sustainable practices creates a culture of environmental awareness. Engaging stakeholders across the supply chain ensures collective commitment.
Sustainability can also be a competitive advantage, attracting eco-conscious customers and investors.
Example:
A packaging company switched to biodegradable materials and installed solar panels in their factories. They also trained staff on waste segregation and energy conservation, reducing their carbon footprint by 40% over three years and winning multiple sustainability awards.
Conclusion
These problems are a common headache for every business owner or manager. With a deep understanding of the root cause of the problem and its solutions, you can streamline processes, foster collaboration, and boost productivity. With these transformative solutions at your disposal, you can embrace the challenges that lie ahead with confidence.
Stay ahead of the competition, maximize efficiency, and ensure customer satisfaction with our indispensable solution, QodeNEXT, at your disposal. Get in touch with us now to help you make the best choice to manage your fleet and optimize your process!
FAQs: 7 Common Industry Problems and Solutions: Comprehensive Guide
1. List some common industry management problems.
Some common industry management problems include a lack of an efficient and sufficient workforce, problems in inventory management, logistics delays, consumerism trends, etc.
2. How can you tackle labor shortage in your industry?
Here are some solutions to labor shortages in industry management: focus on training existing employees, increasing employee turnover, investing in job marketing, offering remote roles, and using automation technology.
3. How can you tackle logistics delays in your industry?
To tackle logistics delays within the industry, you must adopt advanced technological solutions which offer real-time tracking and visibility of your vehicles.
4. How can you tackle inventory management issues in your industry?
Here are some solutions to inventory management issues in your industry: implementing modern inventory tracking systems, Just in Time (JIT) delivery and ABC analysis.
5. How do industry trends affect your business?
Industries, especially retail and manufacturing ones, struggle with consumerism trends and seasonal demands. This creates unpredictable spikes in demand for certain products.
6. Why is workforce automation important in modern industries?
Automation improves efficiency, reduces manual errors, and allows employees to focus on higher-level tasks.
7. What is ABC Analysis in inventory management?
It’s a method of categorizing inventory into A (high value), B (moderate value), and C (low value) items to prioritize management efforts.
8. How does real-time tracking benefit logistics?
It provides live updates on shipments, prevents delays, and improves transparency and customer satisfaction.
9. What are some challenges in implementing new technologies?
Resistance from employees, high costs, and lack of training can be major barriers.
10. How can data analytics improve demand forecasting?
By identifying buying patterns and trends, businesses can make informed stocking and pricing decisions.
11. What are the long-term benefits of going green?
Reduced environmental impact, improved brand reputation, cost savings, and compliance with regulations.






